- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Study highlights noninvasive hearing aid
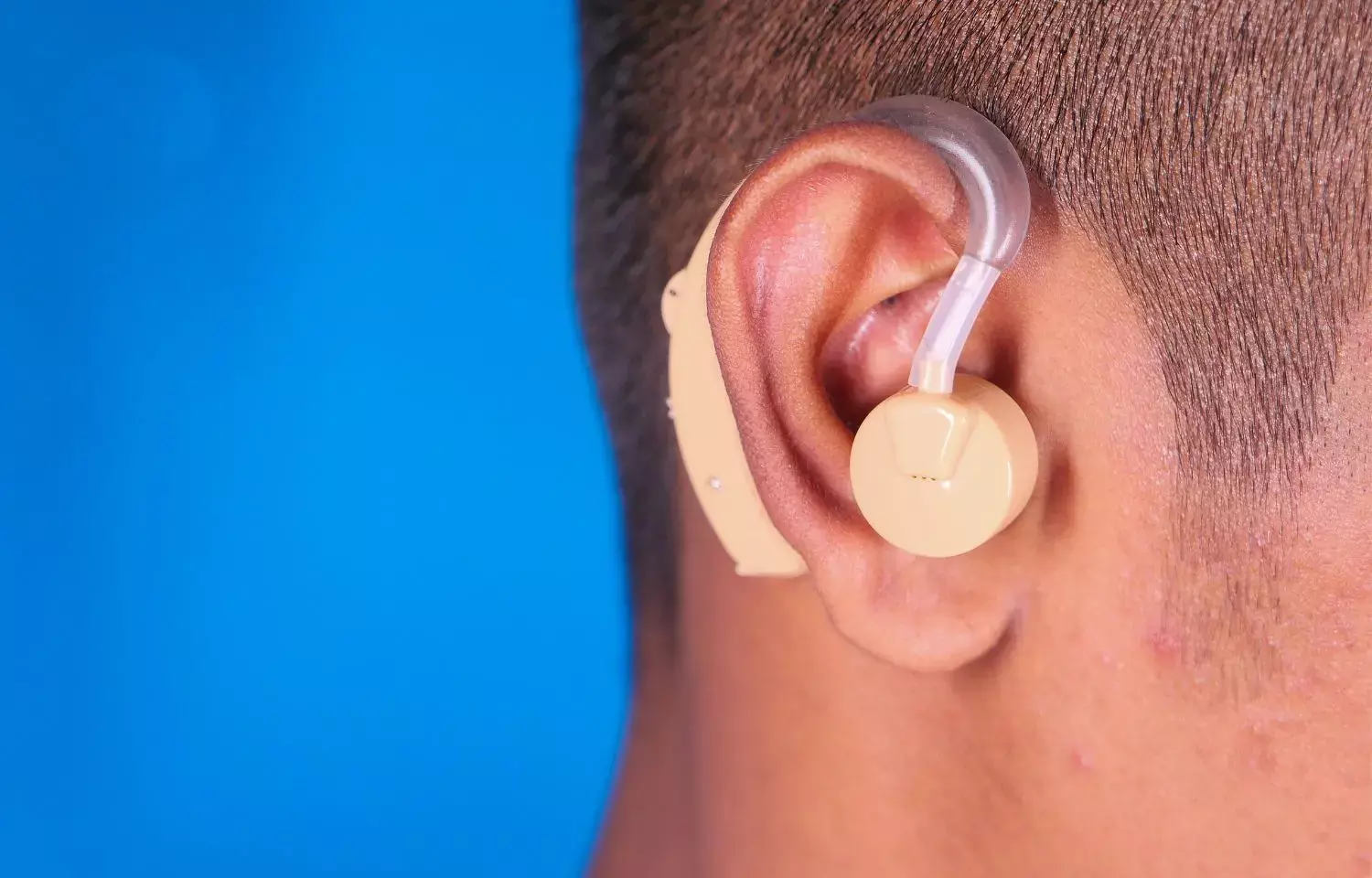
A study from researchers at Wake Forest University School of Medicine highlights a new approach in addressing conductive hearing loss. A team of scientists, led by Mohammad J. Moghimi, Ph.D., assistant professor of biomedical engineering, designed a new type of hearing aid that not only improves hearing but also offers a safe, non-invasive alternative to implantable devices and corrective surgeries.
The study recently published in Communications Engineering, a Nature Portfolio journal.
Conductive hearing loss, which most commonly happens in childhood, occurs when sounds do not reach the inner ear. Sound waves are blocked in the outer or middle ear due to ear infections, blockages or structural abnormalities.
“Treatment for conductive hearing loss can include corrective surgeries and implantable hearing aids, which can be very invasive, especially for pediatric patients,” Moghimi said. “Flexible hearing aids offer a noninvasive alternative.”
To produce vibrations strong enough to reach the cochlea, the part of the inner ear responsible for hearing, the research team designed a flexible hearing aid. The device uses micro-epidermal actuators to create vibrations on the skin behind the ear, which then travel directly to the inner ear, bypassing the ear canal.
For the study, 10 participants between the ages of 19 and 39 wore earplugs and earmuffs to simulate conductive hearing loss. Researchers then tested arrays of the actuators to enhance the vibration strength, improve the quality of sounds and control the direction of the vibrations.
“We found that using an array of these actuators, rather than a single one, significantly enhances the strength and quality of the vibrations, leading to better hearing outcomes,” Moghimi said.
Moghimi also noted that improving hearing in children can reduce delays in language and speech development and boost educational development.
“This technology has the potential to improve the quality of life for children with hearing impairments and transform the way we approach pediatric hearing aids,” Moghimi said.
The research team will next focus on a larger study to further evaluate the efficacy and safety of the device in children and adults.
Reference:
Lim, E., Redleaf, M. & Moghimi, M.J. Array of micro-epidermal actuators for noninvasive pediatric flexible conductive hearing aids. Commun Eng 4, 28 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44172-025-00369-7.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


