- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Three D printed models help plan open Laryngotracheal surgery in children, Finds study
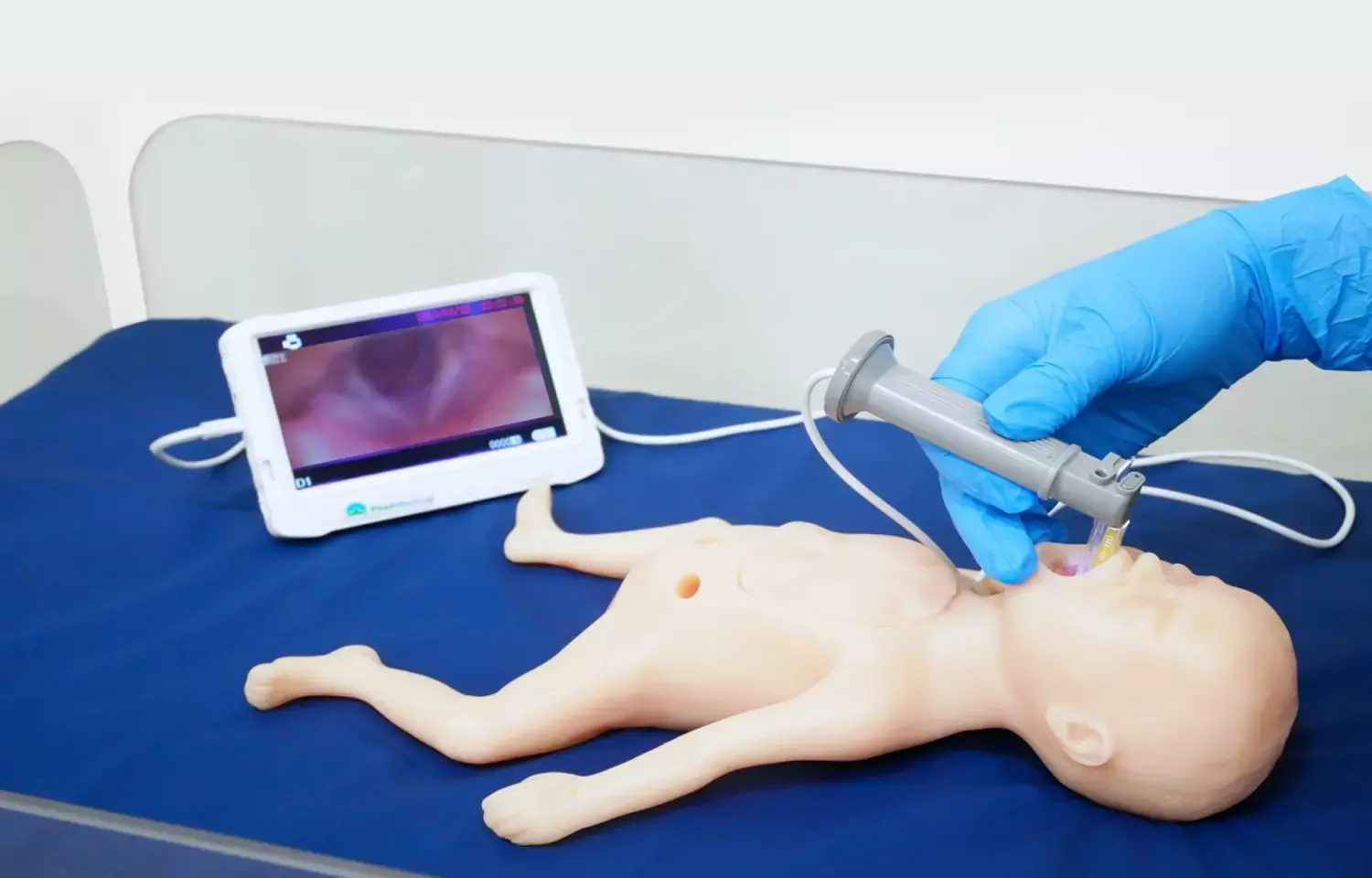
Preoperative planning of open laryngotracheal surgery is important for achieving good results. A recent research revealed that patient-specific three-dimensional printed models of children's upper airways were scored by pediatric airway surgeons as being moderately to very important for preoperative planning of open laryngotracheal surgery.
The study is published in the Journal of Otolaryngology- Head and Neck Surgery.
Oshri Wasserzug and colleagues from the Pediatric Otolaryngology Unit, Dana-Dwek Children's Hospital, Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, Israel examined the surgeon's perception of the importance of using life size 3D printed models of the pediatric airway on surgical decision making.
Life-size three-dimensional models of the upper airway were created based on CT images of children scheduled for laryngotracheal-reconstruction and cricotracheal resection with anastomosis.
Five pediatric airway surgeons evaluated the three-dimensional models for determining the surgical approach, incision location and length, graft length, and need for single or double-stage surgery of seven children (median age 4.4 years, M:F ratio 4:3).
The authors rated the importance of the three-dimensional model findings compared to the direct laryngoscopy videos and CT findings for each domain on a validated Likert scale of 1–5.
It was observed that the mean rating for all domains was 3.6 ± 0.63 ("moderately important" to "very important"), and the median rating was 4 ("very important"). Also, there was full agreement between raters for length of incision and length of graft.
Furthermore, the between-rater agreement was 0.608 ("good") for surgical approach, 0.585 ("moderate") for incision location, and 0.429 ("moderate") for need for single- or two-stage surgery.
Hence, the investigators concluded that patient-specific three-dimensional printed models of children's upper airways were scored by pediatric airway surgeons as being moderately to very important for preoperative planning of open laryngotracheal surgery.
However, large–scale, objective outcome studies are warranted to establish the reliability and efficiency of these models, they added.
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


