- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
CT colonography not recommended for colorectal cancer screening: ACP updated guidelines
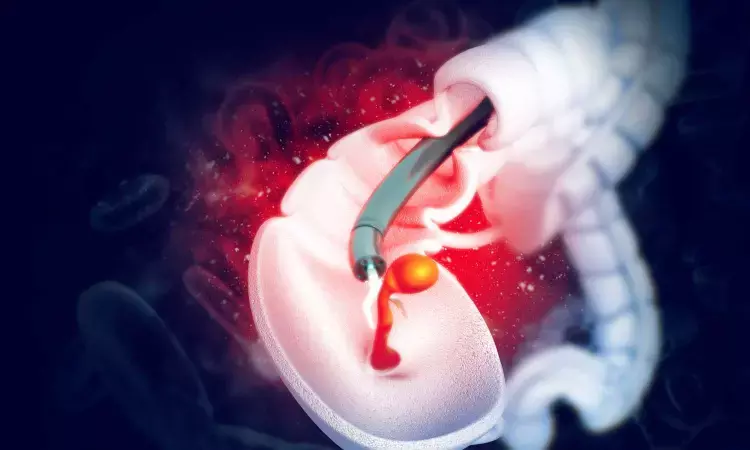
USA: The American College of Physicians (ACP) has released a guidance statement for screening for colorectal cancer in asymptomatic average-risk adults. It suggests starting screening at age 50. The guidelines have recommend not to use stool DNA, computed tomography colonography, capsule endoscopy, urine, or serum screening tests for colorectal cancer.
The guidance, published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, is based on a critical review of existing clinical guidelines and evidence reviews and modelling studies used to develop those guidelines.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the fourth highest in incidence and second in mortality among cancers in the U.S. The goal of this ACP guidance statement is to help guide physicians on when to start and stop screening, and on the selection of type and frequency of screening tests in asymptomatic, average-risk adults. ACP’s guidance is for adults at average risk for CRC who do not have symptoms. It does not apply to adults with a family history of colorectal cancer, a long-standing history of inflammatory bowel disease, genetic syndromes such as familial cancerous polyps, a personal history of previous colorectal cancer or benign polyps, or other risk factors. Physicians should perform an individualized risk assessment for CRC in all adults.
In this updated guidance, ACP suggests that clinicians:
• Start screening for colorectal cancer in asymptomatic average-risk adults at age 50 years.
• Consider not screening asymptomatic average-risk adults between the ages of 45 to 49. Clinicians should discuss the uncertainty around benefits and harms of screening in this population.
• Stop screening for colorectal cancer in asymptomatic average-risk adults older than 75 years or in asymptomatic average-risk adults with a life expectancy of 10 years or less.
• Select a screening test for colorectal cancer in consultation with the patient based on a discussion of benefits, harms, costs, availability, frequency, and patient values and preferences.
• Select among screening tests for colorectal cancer: a fecal immunochemical or high-sensitivity guaiac fecal occult blood test every 2 years, colonoscopy every 10 years, or flexible sigmoidoscopy every 10 years plus a fecal immunochemical test every 2 years.
• Should not use stool DNA, computed tomography colonography, capsule endoscopy, urine, or serum screening tests for colorectal cancer.
The net benefit of colorectal cancer screening is much less favorable in average-risk adults between ages 45 to 49 years than 50 to 75 years. Although there has been a small increase in CRC incidence among individuals aged 45 to 49 years, the incidence is much lower than in individuals aged 50 to 64 years and 65 to 74 years. Harms associated with CRC screening include cardiovascular and gastrointestinal events (e.g., serious bleeding, perforation, myocardial infarction, angina), unnecessary follow-ups, and costs for findings deemed clinically unimportant.
Reference:
Amir Qaseem, Curtis S. Harrod, Carolyn J. Crandall, Screening for Colorectal Cancer in Asymptomatic Average-Risk Adults: A Guidance Statement From the American College of Physicians, https://doi.org/10.7326/M23-0779.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


