- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Acupuncture improves chronic indigestion disorder finds clinical trial
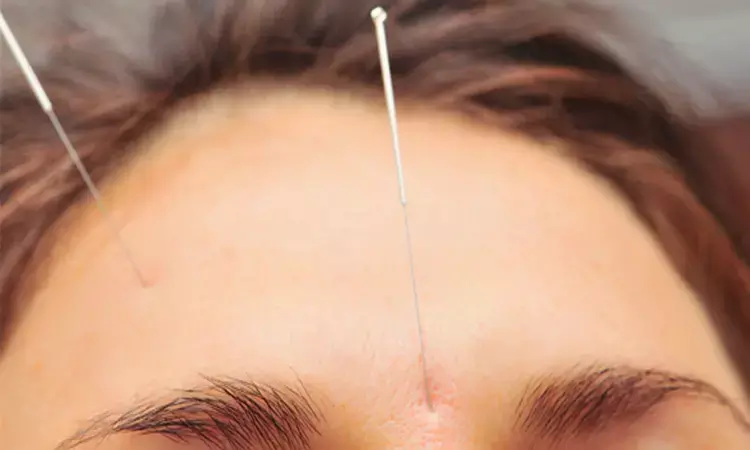
The evidence for different frequencies of acupuncture treatment in postprandial distress syndrome (PDS) is insufficient.
Researchers conducted a multicenter 2-group, randomized clinical trial to assess the efficacy of acupuncture versus sham acupuncture in patients with PDS in 5 tertiary hospitals in China.
They found that a 4-week course of acupuncture increased self-reported relief and improvement of symptoms for patients with a subtype of indigestion known as postprandial distress syndrome (PDS). The effects of acupuncture persisted through the 12-week follow-up without symptom relapse or rebound. Findings from a randomized clinical trial are published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Postprandial distress syndrome, a condition characterized by bothersome early fullness after eating and upper abdominal bloating, places a substantial burden on the health care system because of its high prevalence in a relatively young patient population and the chronic relapsing nature of its symptoms. The condition is reported to have a great negative effect on health-related quality of life, which makes finding an effective treatment imperative. Previous studies on acupuncture have been limited by the small number of participants and poor study quality.
Researchers from the Beijing University of Chinese Medicine randomly assigned 278 Chinese patients with PDS to 12 sessions of acupuncture or sham acupuncture over 4 weeks and then compared the proportion of patients in each group who reported "extreme improvement" or "improvement" in their stomach symptoms as well as the proportion of patients who experienced complete resolution of their symptoms. They found that a significantly higher proportion of patients in the acupuncture group experienced overall improvement or elimination of their symptoms than in the sham acupuncture group. The improvement was sustained for at least 12 weeks after the final acupuncture treatment and there were no serious adverse events among the study patients.
For more details click on the link: http://annals.org/aim/article/doi/10.7326/M19-2880
Hina Zahid Joined Medical Dialogue in 2017 with a passion to work as a Reporter. She coordinates with various national and international journals and association and covers all the stories related to Medical guidelines, Medical Journals, rare medical surgeries as well as all the updates in the medical field. Email: editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


