- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Innovative Gastric Cancer Screening Approach Shows Promising Results in Randomized Controlled Trial
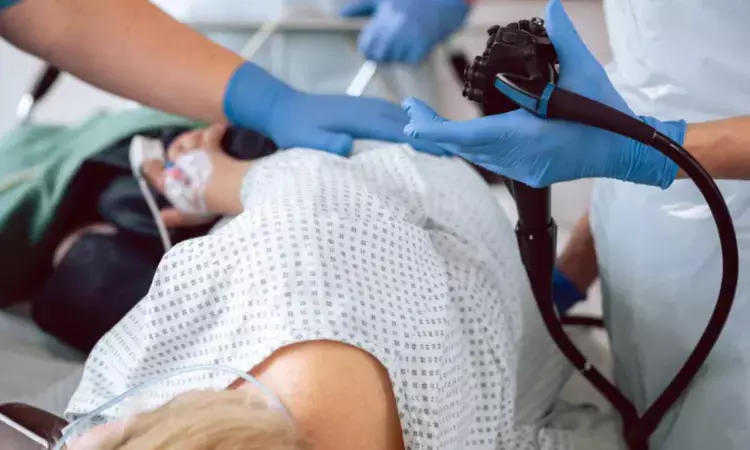
In a groundbreaking randomized controlled trial conducted in Yurihonjo and Nikaho city, Akita Prefecture, researchers have unveiled a new approach to gastric cancer (GC) screening that could revolutionize early detection and treatment outcomes. The study compared the efficacy of two screening methods, Ba-Endo (barium photofluorography following upper gastrointestinal endoscopy) and ABC-Endo group (upper gastrointestinal endoscopy according to serological stratification) and found that gastric cancers could be better cured by endoscopic resection alone in the ABC-Endo group.
The study results were published in the journal Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.
Attempts have been undertaken to create an endoscopic screening system that integrates serological gastric cancer (GC) risk stratification, specifically the ABC classification, in conjunction with the yearly population-based GC screening using barium. The study, spanning five years and involving 1,206 participants, compared the efficacy of two screening methods: the Ba-Endo group, which underwent annual barium tests followed by detailed endoscopic examinations, and the ABC-Endo group.
The participants were carefully randomized using the minimization method, with sex and age considered as key allocation factors. Over the course of the study, the Ba-Endo group adhered to annual barium tests, while the ABC-Endo group underwent esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) at varying intervals, including Group A (EGD only at entry), Group B (EGD once every 3 years), Group C (EGD once every 2 years), and Group D (EGD every year).
Findings:
- Results from the trial revealed that both groups exhibited a similar overall GC detection rate of 1.9%, with 24 detected GC lesions.
- The Ba-Endo and ABC-Endo groups demonstrated detection rates of 2.0% and 1.8%, respectively, showing no statistically significant differences between them (P=1.0).
- However, a remarkable finding emerged when analyzing the efficacy of endoscopic resection in treating the detected GCs.
- Notably, the study found that the rate of GCs cured by endoscopic resection alone was 41.6% in the Ba-Endo group. Surprisingly, the ABC-Endo group displayed a significantly higher rate, reaching 90.9% (P=0.02).
- This groundbreaking outcome suggests that the ABC-Endo approach, which tailors endoscopy intervals based on individual risk factors, holds substantial promise in identifying and successfully treating GCs through less invasive means.
These results could potentially reshape the landscape of gastric cancer screening programs worldwide. The personalized ABC-Endo strategy not only demonstrated comparable detection rates to the traditional Ba-Endo method but also exhibited a clear advantage in terms of successful endoscopic resection, offering patients a less invasive and more effective treatment option for early-stage gastric cancers. Further research and validation are crucial, but the promising outcomes of this trial suggest a step forward in the ongoing fight against gastric cancer.
Further reading: Kusano C, Gotoda T, Ishikawa H, Suzuki S, Ikehara H, Matsuyama Y. Gastric Cancer Detection Rates using Gastrointestinal Endoscopy with Serological Risk Stratification: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Gastrointest Endosc. Published online January 23, 2024. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2024.01.022
BDS, MDS
Dr.Niharika Harsha B (BDS,MDS) completed her BDS from Govt Dental College, Hyderabad and MDS from Dr.NTR University of health sciences(Now Kaloji Rao University). She has 4 years of private dental practice and worked for 2 years as Consultant Oral Radiologist at a Dental Imaging Centre in Hyderabad. She worked as Research Assistant and scientific writer in the development of Oral Anti cancer screening device with her seniors. She has a deep intriguing wish in writing highly engaging, captivating and informative medical content for a wider audience. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


