- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Risk of liver fibrosis associated with methotrexate use likely to be overestimated
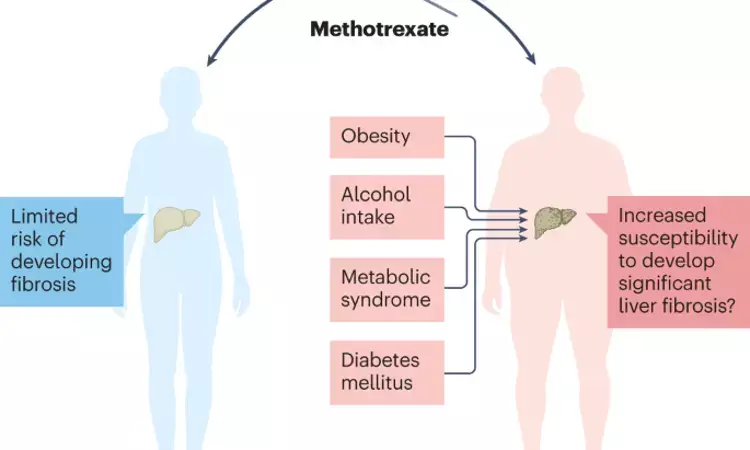
Risk of liver fibrosis associated with methotrexate use likely to be overestimated suggests a new study published in the Journal Of Hepatology
The risk of significant liver fibrosis from prolonged methotrexate (MTX) exposure has been estimated at around 5%, prompting intensive monitoring strategies. However, the evidence is derived from retrospective studies that under-reported risk factors for liver disease. We evaluated the risk of long-term MTX therapy on liver fibrosis in a longitudinal cohort study using two non-invasive markers.
Between 2014-2021, adult patients diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or psoriasis for ≥2 years were recruited prospectively from six UK sites. The MTX group included patients who received MTX for ≥6 months, whereas the unexposed group included those who never received MTX. All patients underwent full liver profiling, with transient elastography (TE) and enhanced liver fibrosis (ELF) marker measurements.
Results
A total of 999 patients (mean age 60.8 ± 12 years, 62.3% females) were included. Of 976 with valid TE values, 149 (15.3%) had liver stiffness ≥7.9 kPa. Of 892 with a valid ELF, 262 (29.4%) had ELF ≥9.8. Age and BMI were independently associated with elevated liver stiffness and ELF. Neither MTX cumulative dose nor duration was associated with elevated liver stiffness. Diabetes was the most significant risk factor associated with liver stiffness ≥7.9 kPa (adjusted odds ratio = 3.19; 95% CI 1.95–5.20; p <0.001). Regular use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs showed the strongest association with ELF ≥9.8 (odds ratio = 1.76; 95% CI 1.20–2.56; p = 0.003), suggesting the degree of joint inflammation in RA may confound ELF as a non-invasive marker of liver fibrosis.
The risk of liver fibrosis attributed to MTX itself might have been previously overestimated; there is a need to consider modifying current monitoring guidelines for MTX. Current guidelines recommend intensive (2-3 monthly) monitoring strategies for patients on long-term methotrexate therapy due to the potential risk of liver fibrosis. Evaluation of the association using two validated non-invasive markers of liver fibrosis, liver stiffness and enhanced liver fibrosis score, in a large cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis or psoriasis shows that the reported risk has previously been overestimated. The clinical focus should be to improve patients’ metabolic risk factors, diabetes and BMI, that are independently associated with liver stiffness. There is a need to consider modifying current treatment monitoring guidelines for methotrexate.
Reference:
Edmond Atallahm, Jane I. Grove, Colin Crooks, Richard J. Aspinall, Ruth Murphy, Guruprasad P. Aithal. Risk of liver fibrosis associated with long-term methotrexate therapy may be overestimated. Journal Of HepatologyPublished:January 23, 2023DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2022.12.034
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


