- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
AI Pilot Study Revolutionizes Pulp Stone Detection in Panoramic Radiographies
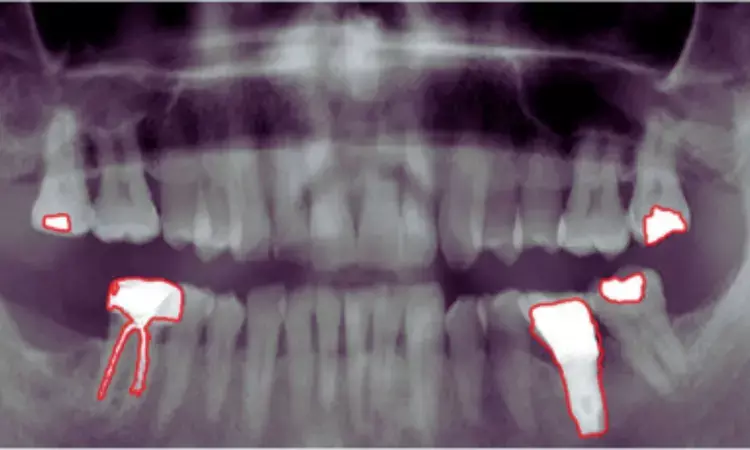
Turkey: In a groundbreaking advancement in dental imaging, researchers have successfully utilized automatic deep-learning algorithms to detect pulp stones in panoramic radiographies. This pioneering AI pilot study, published in Diagnostics, heralds a new era in dental diagnostics, offering potential improvements in accuracy and efficiency in identifying these small calcified structures within teeth.
The study showed the potential of using artificial intelligence (AI)-supported clinical decision-support system software to increase the efficiency and effectiveness of dentists.
"In the near future, the integration of AI-supported clinical decision support systems may augment the capabilities of clinicians in detecting pulp stones and other anomalies on panoramic radiographs, leading to improved treatment outcomes and patient care," the researchers wrote.
Pulp stones, or denticles, are mineralized masses that develop within the pulp chamber or root canals of teeth. While often asymptomatic, pulp stones can pose challenges for dentists during diagnosis and treatment planning, particularly when obscured by surrounding tissues or overlapping structures in traditional radiographic images.
Kaan Orhan, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry, Ankara University, Ankara, Turkey, and colleagues aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of employing a deep learning approach for the automated detection of pulp stones in panoramic imaging.
For this purpose, a comprehensive dataset incusing 2409 panoramic radiography images (7564 labels) underwent labeling using the CranioCatch labeling program, developed in Eskişehir, Turkey. The dataset was stratified into three distinct subsets: training (n = 1929, 80% of the total), validation (n = 240, 10% of the total), and test (n = 240, 10% of the total) sets.
A 3 × 3 clash operation was applied to the images to optimize the visual clarity of labeled regions. The YOLOv5 architecture was employed for artificial intelligence modeling, yielding F1, sensitivity, and precision metrics of 0.7892, 0.8026, and 0.7762, respectively, during the evaluation of the test dataset.
Among deep learning-based AI algorithms applied to panoramic radiographs, using numerical identification for detecting pulp stones has achieved remarkable success. The success rates of training models are expected to increase using datasets consisting of larger images.
"The successful application of deep learning algorithms for detecting pulp stone on panoramic radiographs holds significant clinical implications," the researchers wrote.
"Further research optimizing these AI-based tools with larger datasets holds the potential to enhance diagnostic efficiency and accuracy in dental practice."
In conclusion, successful pulp stone detection with automatic deep learning in panoramic radiography represents a significant leap forward in dental imaging technology. This AI pilot study is promising for enhanced diagnostic accuracy, efficiency, and improved patient care in dentistry.
Reference:
Altındağ, A., Bahrilli, S., Çelik, Ö., Bayrakdar, İ. Ş., & Orhan, K. (2023). The Detection of Pulp Stones with Automatic Deep Learning in Panoramic Radiographies: An AI Pilot Study. Diagnostics, 14(9), 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics14090890
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


