- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Medical Breakthrough: First-ever 3-D Colour X-ray performed on a human
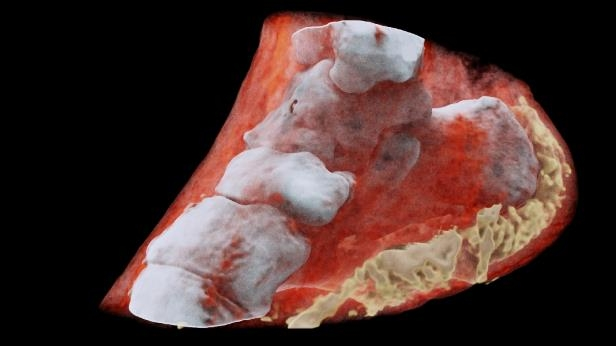
The machine's "small pixels and accurate energy resolution meant that this new imaging tool is able to get images that no other imaging tool can achieve," said developer Phil Butler of the University of Canterbury.
Paris: New Zealand scientists have performed the first-ever 3-D, colour X-ray on a human, using a technique that promises to improve the field of medical diagnostics, said Europe's CERN physics lab which contributed imaging technology.
The new device, based on the traditional black-and-white X-ray, incorporates particle-tracking technology developed for CERN's Large Hadron Collider, which in 2012 discovered the elusive Higgs Boson particle.
"This colour X-ray imaging technique could produce clearer and more accurate pictures and help doctors give their patients more accurate diagnoses," said a CERN statement.
The machine's "small pixels and accurate energy resolution meant that this new imaging tool is able to get images that no other imaging tool can achieve," said developer Phil Butler of the University of Canterbury.
According to the CERN, the images very clearly show the difference between bone, muscle and cartilage, but also the position and size of cancerous tumours, for example.
The technology is being commercialised by New Zealand company MARS Bioimaging, linked to the universities of Otago and Canterbury which helped develop it.
Paris: New Zealand scientists have performed the first-ever 3-D, colour X-ray on a human, using a technique that promises to improve the field of medical diagnostics, said Europe's CERN physics lab which contributed imaging technology.
The new device, based on the traditional black-and-white X-ray, incorporates particle-tracking technology developed for CERN's Large Hadron Collider, which in 2012 discovered the elusive Higgs Boson particle.
"This colour X-ray imaging technique could produce clearer and more accurate pictures and help doctors give their patients more accurate diagnoses," said a CERN statement.
The CERN technology, dubbed Medipix, works like a camera detecting and counting individual sub-atomic particles as they collide with pixels while its shutter is open. This allows for high-resolution, high-contrast pictures.
The machine's "small pixels and accurate energy resolution meant that this new imaging tool is able to get images that no other imaging tool can achieve," said developer Phil Butler of the University of Canterbury.
According to the CERN, the images very clearly show the difference between bone, muscle and cartilage, but also the position and size of cancerous tumours, for example.
The technology is being commercialised by New Zealand company MARS Bioimaging, linked to the universities of Otago and Canterbury which helped develop it.
Medical Dialogues Bureau consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Next Story


