- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Severe burning pain in legs after taking migraine medicine: NEJM Case report
Courtesy NEJM
Dr Aravind Reghukumar at Government Medical College, Thiruvananthapuram, Thiruvananthapuram, India and Dr Reshma Benson have reported a rare case severe burning pain in legs.The case has been published in New England journal of Medicine.
The symptoms of the patient fell into category of Ergotism which was precipitated by taking oral ergotamine for migraine and vasospastic limb ischemia caused by Ritonavir which the patient had been taking as part of her HIV treatment. Usually Ergotism results from consumption of the ergot body in rye or other grains infected by a parasitic fungus of the genus Claviceps. Chronic ergot poisoning (ergotism) was rife during the Middle Ages due to the consumption of contaminated rye. Because of the burning pain, it was known as "ignis sacer" (holy fire), "ignis infernalis" (hell's fire) and St. Anthony's fire.
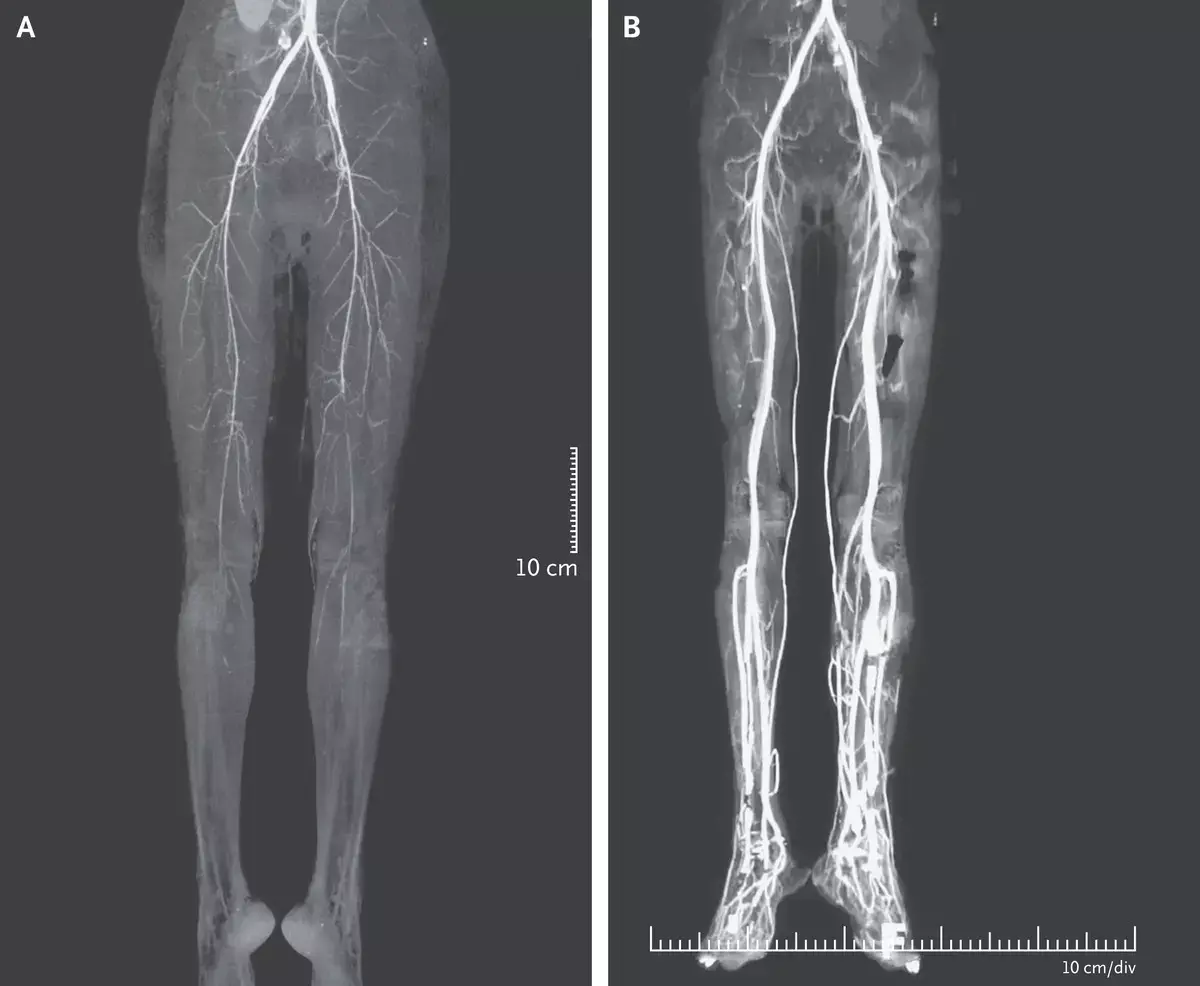
According to the history, a 24-year-old woman presented to the outpatient clinic with a 2-day history of severe, burning leg pain. She had a history of congenital infection with the human immunodeficiency virus, for which she was taking tenofovir, emtricitabine, and lopinavir–ritonavir. Four days before presentation she had also started taking ergotamine twice daily for a migraine headache. The pain in the legs extended from the toes to the midthigh and was accompanied by discoloration of the feet and difficulty walking. On examination, both legs were cold, with nonpalpable popliteal and dorsalis pedis pulses. Computed tomographic (CT) angiography revealed diffuse, symmetric, luminal narrowing of the arteries below the external iliac artery in both legs (Panel A). A diagnosis of ergotism was suspected. Ritonavir inhibits the enzyme CYP3A4, leading to increased serum levels of ergotamine and thereby causing vasospastic limb ischemia. Treatment with intravenous prostaglandin and unfractionated heparin was initiated. The pain subsided, and patient's legs became warmer, but she underwent amputation of the left second toe owing to gangrene. A repeat CT angiogram obtained 2 weeks after presentation showed improved perfusion in both legs (Panel B).
For further reference log on to:
DOI: 10.1056/NEJMicm1911089
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


