- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Buttonhole cannulation better than rope ladder cannulation for making AV fistula for dialysis
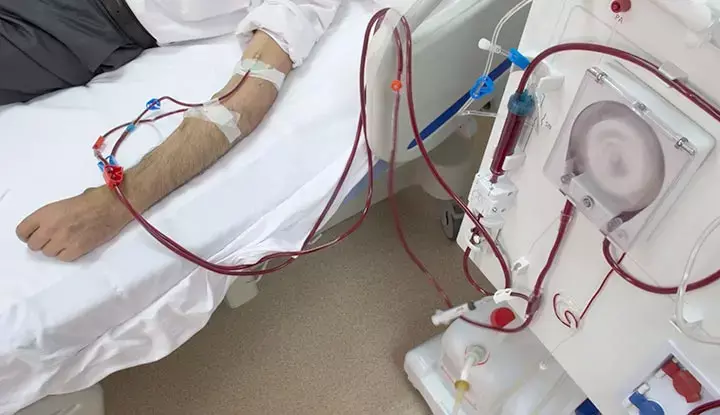
Buttonhole cannulation better than over rope ladder cannulation for arteriovenous fistula, finds a new study. Therefore it should be recommended as a routine procedure for hemodialysis.
The study has been published in the journal Medicine.
Safe and effective arteriovenous fistula (AVF) puncture techniques must be used to reduce harm to hemodialysis patients. The relative benefits of buttonhole (BH) cannulation over those of rope ladder (RL) cannulation for AVF remain unclear and inconsistent.
This systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. Literature searches were conducted in June 2020 in multiple scientific databases including Cochrane library, CINAHL, PubMed/ Medline, Airiti Library, National Digital Library of Theses and Dissertations in Taiwan, Google scholar, Embase, and ProQuest. They included all randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and clinical controlled trials (CCTs) that explored the efficacy of BH cannulation in hemodialysis patients. These included reports published in either English or Chinese that enrolled adults aged 18 years or older who underwent hemodialysis using an autogenous AVF. Studies that showed poor design, such as the use of a self-control group or no control group, were excluded from the analysis. The critical appraisal skills program checklist for RCTs was used to assess the quality of the evidence and RevMan software was used to perform the meta-analysis.
Results:
Fifteen studies (11 RCTs and 4 CCTs) met the inclusion criteria and were used for the meta-analysis. Meta-analysis showed that BH cannulation significantly reduced aneurysm formation (RR = 0.18, 95% confidence interval, thrombosis formation, and hematoma and showed no differences in AVR infection compared to RL cannulation.
Thus, given the benefits of BH, this meta-analysis found that BH cannulation should be recommended as a routine procedure for hemodialysis but that hospitals and hemodialysis clinics should strengthen staff knowledge and skills of BH cannulation to reduce the risk of AVF infection.
Reference:
Wang, Li-Ping MSNa; Tsai, Li-Hwa MSNa; Huang, Hisang-Yun MSNa; Okoli, Chizimuzo PhDb; Guo, Su-Er PhDc,d,e,*. Effect of buttonhole cannulation versus rope-ladder cannulation in hemodialysis patients with vascular access: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized/clinical controlled trials. Medicine: July 22, 2022 - Volume 101 - Issue 29 - p e29597
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000029597
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


