- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
DOACs Show Promise in Treating Splanchnic Vein Thrombosis
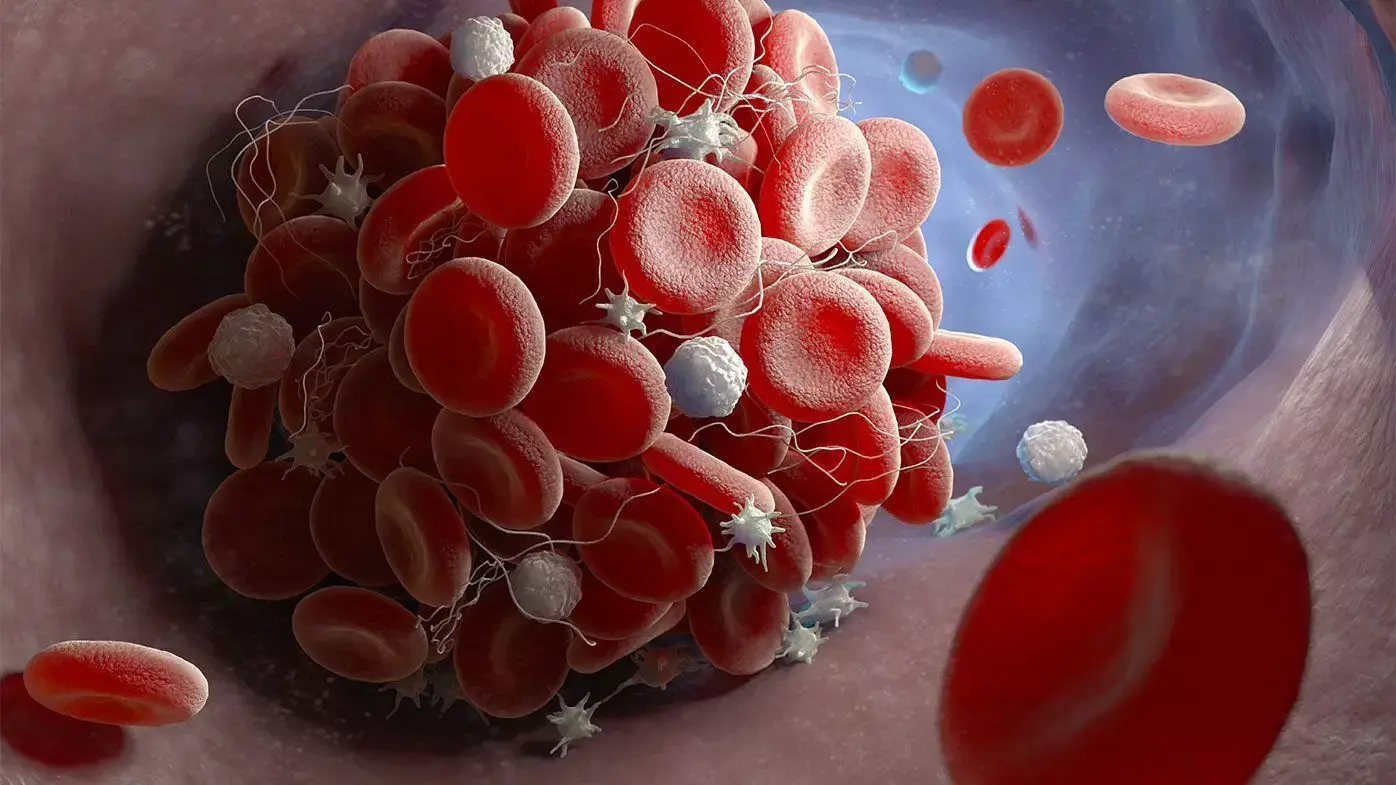
Splanchnic vein thrombosis (SVT), an uncommon type of venous thromboembolism affecting the splanchnic venous system, has posed challenges in terms of its management due to limited evidence. However, a recent comprehensive review and meta-analysis published in Thrombosis Research by Allen Li and colleagues have shed new light on the efficacy and safety of treatment options, particularly focusing on direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs).
The study's primary goal was to assess the effectiveness and safety of DOACs in comparison to low-molecular-weight heparins (LMWHs), vitamin K antagonists (VKAs), or no anticoagulation treatment for SVT.
● DOACs emerged as a promising treatment option. In non-cirrhotic patients, DOACs displayed superior efficacy compared to VKAs, achieving a significant complete recanalization of affected vessels (OR = 4.33; 95% CI: 2.4, 7.83).
● In cirrhotic patients, DOACs were also more effective than no anticoagulation treatment (OR = 3.86; 95% CI: 1.49, 10.03).
● One of the most remarkable findings was the reduced risk of major bleeding associated with DOACs. Non-cirrhotic patients on DOACs experienced significantly less major bleeding compared to those on observation, LMWHs, and VKAs (OR = 0.09; 95% CI: 0.03, 0.29).
● DOACs did not show a significant difference in major bleeding when compared to observation, LMWHs, or VKAs in cirrhotic patients.
The study's results suggest that DOACs could be a favourable alternative to traditional treatments like VKAs and LMWHs for non-cirrhotic patients with SVT. However, further research is needed, including larger studies that account for various SVT causes, patient risk factors, and overall bleeding risks.
This breakthrough research not only provides valuable insights into the management of SVT but also opens doors for potential advancements in the treatment of this condition. As medical experts delve deeper into the intricacies of SVT and its treatment options, patient care could see significant improvements, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for those affected.
Reference:
Li, A., Zhang, M. C., Li, P., Eshaghpour, A., Li, K., Carrier, M., Wells, P., & Crowther, M. A. (2023). Direct oral anticoagulants for the treatment of splanchnic vein thrombosis – A systematic review and meta-analysis. Thrombosis Research, 229, 209–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2023.06.003
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


