- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Lowering blood insulin levels may even help lower risk of getting COVID-19, finds study
Keeping blood insulin levels within strict, healthy parameters is a daily goal for people with diabetes.
Lowering blood insulin levels may even help lower risk of getting COVID-19, find researchers from Japan in a new study.
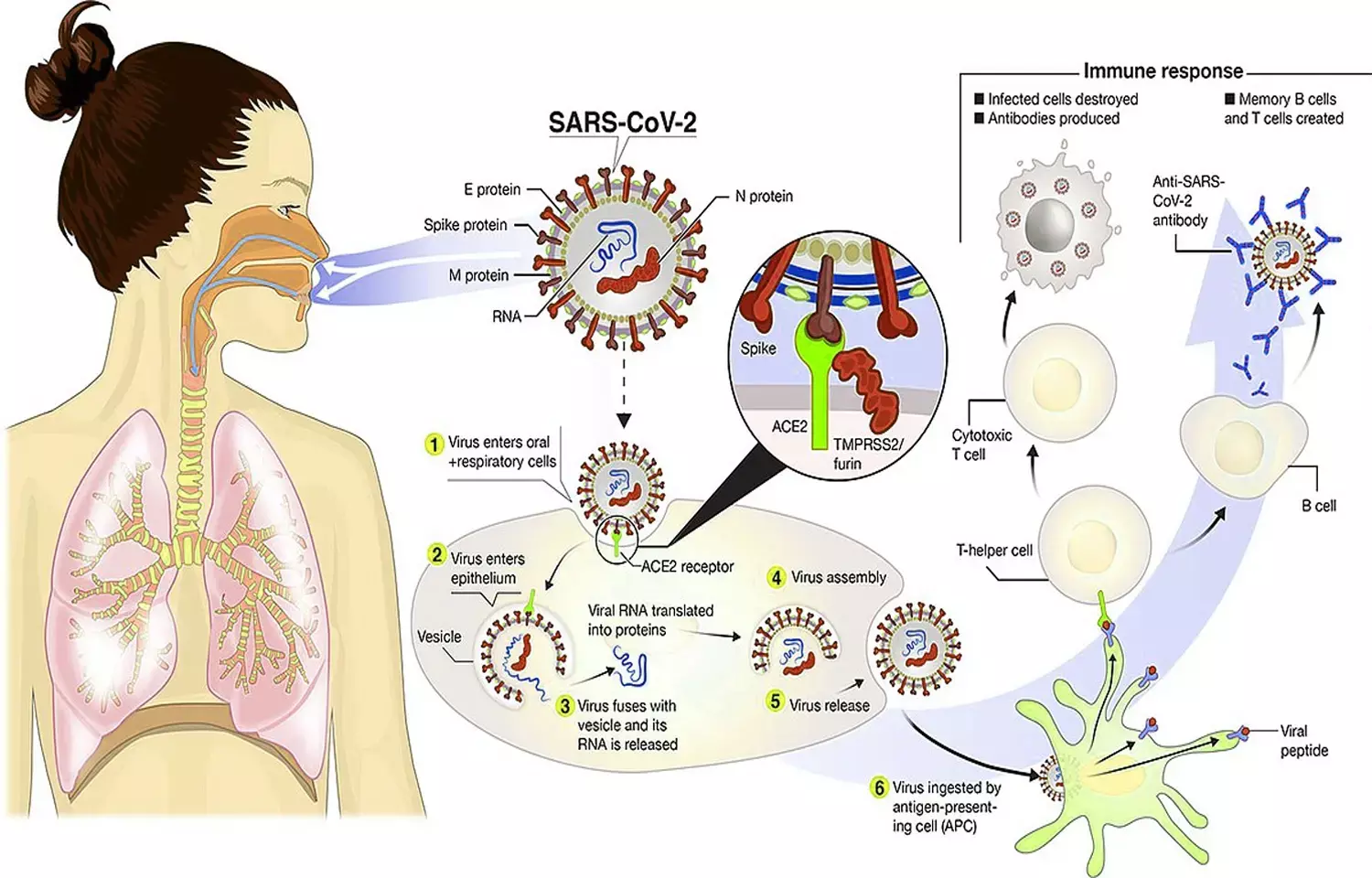
In a study published this month in Diabetes, researchers from Osaka University have revealed that a protein called GRP78 helps the virus that causes COVID-19 bind to and enter cells. GRP78 is a protein that is found in adipose tissue (i.e., fat). Older, obese, and diabetic people are all more vulnerable to COVID-19 and, while the reasons for this are still not completely clear, the team from Osaka University sheds some light on this issue.
"It was recently suggested that adipose tissue might be a major reservoir for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19," says lead author of the study Jihoon Shin. "Because of this, we wanted to investigate whether there is any link between the excess adipose tissue in older, obese, and diabetic patients and their vulnerability to COVID-19."
To do this, the researchers looked at GRP78, which has recently been suggested to be involved in the interaction of SARS-CoV-2 with human cells. The major method by which SARS-CoV-2 enters human cells is by a spike protein on the viral surface binding to a human cell-surface protein called angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). Shin and colleagues discovered that the spike protein can also directly bind to GRP78, and that the presence of GRP78 increases the binding with ACE2. To get an idea of GRP78's involvement in COVID-19 vulnerability they investigated how much GRP78 protein is present in tissues from older, obese, and diabetic patients.
"The results were very clear," explains senior author Iichiro Shimomura. "GRP78 gene expression was highly upregulated in adipose tissue, and was elevated with increasing age, obesity, and diabetes."
Aging, obesity, and diabetes are known to be associated with increased blood insulin levels. Therefore, the group wondered whether insulin was involved in GRP78 expression. They found that exposing cells to insulin did induce expression of GRP78. Importantly, they discovered that treatment using widely prescribed anti-diabetic drugs that reduce insulin levels successfully reduce expression level of GRP78. They went a step further and showed that exercise and calorie restriction in a mouse-model also worked to reduce GRP78 levels in adipose tissue.
"Our findings suggest that a high blood insulin level is an important risk factor that can predispose older, obese, and diabetic individuals to COVID-19 infection. As such, controlling blood insulin with pharmacological interventions or with environmental interventions, such as exercise, could help lower these patients' risk," says Shin.
Given the global impact of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, the results from this study provide important insights into how to lower the risk of infection in these vulnerable patients. Reducing GRP78 expression by pharmacological or environmental interventions may improve outcomes in these patients.
In older and obese diabetic patients①, hyperinsulinemia② causes cellular stress and induces the XBP-1-mediated overexpression of GRP78③ in adipose tissue, which promotes localization of GRP78 to the circulation④ and cell surface⑤, not only to endoplasmic reticulum (ER)⑥. GRP78 physically interacts with the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, which may play a number of crucial roles in the viral lifecycle. The interaction of the spike protein with soluble and cell surface GRP78 may facilitate the SARS-CoV-2 binding to and infection of ACE2-expressing host cells. Soluble GRP78 bound to SARS-CoV-2 in the circulation could induce the systemic viral spread and infection. Binding of SARS-CoV-2 to cell surface GRP78 or related stimuli could activate the NF-κB or JNK/STAT3 transcriptional pathway and induce cellular inflammatory responses. SARS-CoV-2 potentially exploits ER-located GRP78 as a molecular chaperone to produce and assemble viral particles, which enables successful viral replication (brown virus indicates newly replicated SARS-CoV-2). The high expression of GRP78 in older and obese diabetic patients may contribute to the COVID-19 progression and severe outcomes
Hina Zahid Joined Medical Dialogue in 2017 with a passion to work as a Reporter. She coordinates with various national and international journals and association and covers all the stories related to Medical guidelines, Medical Journals, rare medical surgeries as well as all the updates in the medical field. Email: editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


