- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
AI holds potential to differentiate between normal and abnormal kidneys in children on SPECT imaging
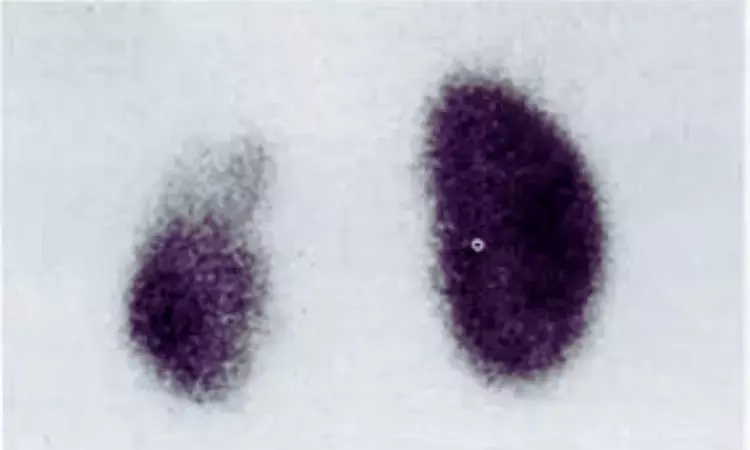
Taiwan: A recent study published in Clinical Radiology has suggested the potential of deep learning (DL) to differentiate normal from abnormal kidneys in children using 99mTc-DMSA SPECT imaging.
In a test, the model developed by C. Lin, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taoyuan, Taiwan, and colleagues, achieved an almost perfect agreement with reads by two experienced experts.
Experimental results indicate that the AI (artificial intelligence) model based on SPECT images has the potential to help nuclear medicine physicians identify kidney defects in children.
"Our findings suggest that deep learning may be used as a computer-aided diagnosis system that assists less-experienced nuclear medicine physicians in the diagnosis of renal cortical defects," the researchers wrote. "Thus, they suggested an AI model that can differentiate between normal and abnormal kidneys "may be of clinical interest" in these patients.
The team investigated the feasibility of using deep learning to differentiate normal from abnormal (or scarred) kidneys using technetium-99m dimercaptosuccinic acid (99mTc-DMSA) single-photon-emission computed tomography (SPECT) in paediatric patients.
For this purpose, the researchers retrospectively reviewed three hundred and one 99mTc-DMSA renal SPECT examinations. 301 patients were randomly split into 261, 20, and 20 for training, validation, and testing data, respectively.
Training of the DL model was done using 3D SPECT images, 2D maximum intensity projections (MIPs), and 2.5-dimensional (2.5D) MIPs (i.e., transverse, sagittal, and coronal views). Each DL model was trained to determine SPECT images as either abnormal or normal. The reference standard was the consensus reading results by two nuclear medicine physicians.
Key findings include:
· The DL model trained by 2.5D MIPs outperformed that trained by either 3D SPECT images or 2D MIPs.
· The accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of the 2.5D model for the differentiation between normal and abnormal kidneys were 92.5%, 90% and 95%, respectively.
· Further analysis revealed a kappa coefficient of 0.85 obtained from the 2.5D model, indicating that it provided an almost perfect agreement with the visual reading results of the two experienced physicians.
The findings were promising, despite this the study was limited by a small number of patient images. They suggested that such DL models ultimately should also apply to adults, including renal transplant donor candidates. They wrote that additional research is warranted.
"The study is the first using DL with Tc-99m DMSA SPECT images to evaluate differentiating normal from abnormal kidneys," the researchers noted.
Reference:
Lin, C., Chang, Y., Chiu, H., Cheng, C., & Huang, H. (2023). Differentiation between normal and abnormal kidneys using 99mTc-DMSA SPECT with deep learning in paediatric patients. Clinical Radiology, 78(8), 584-589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2023.04.015
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


