- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Intradialytic Exercise Improves Health Outcomes in Hemodialysis Patients
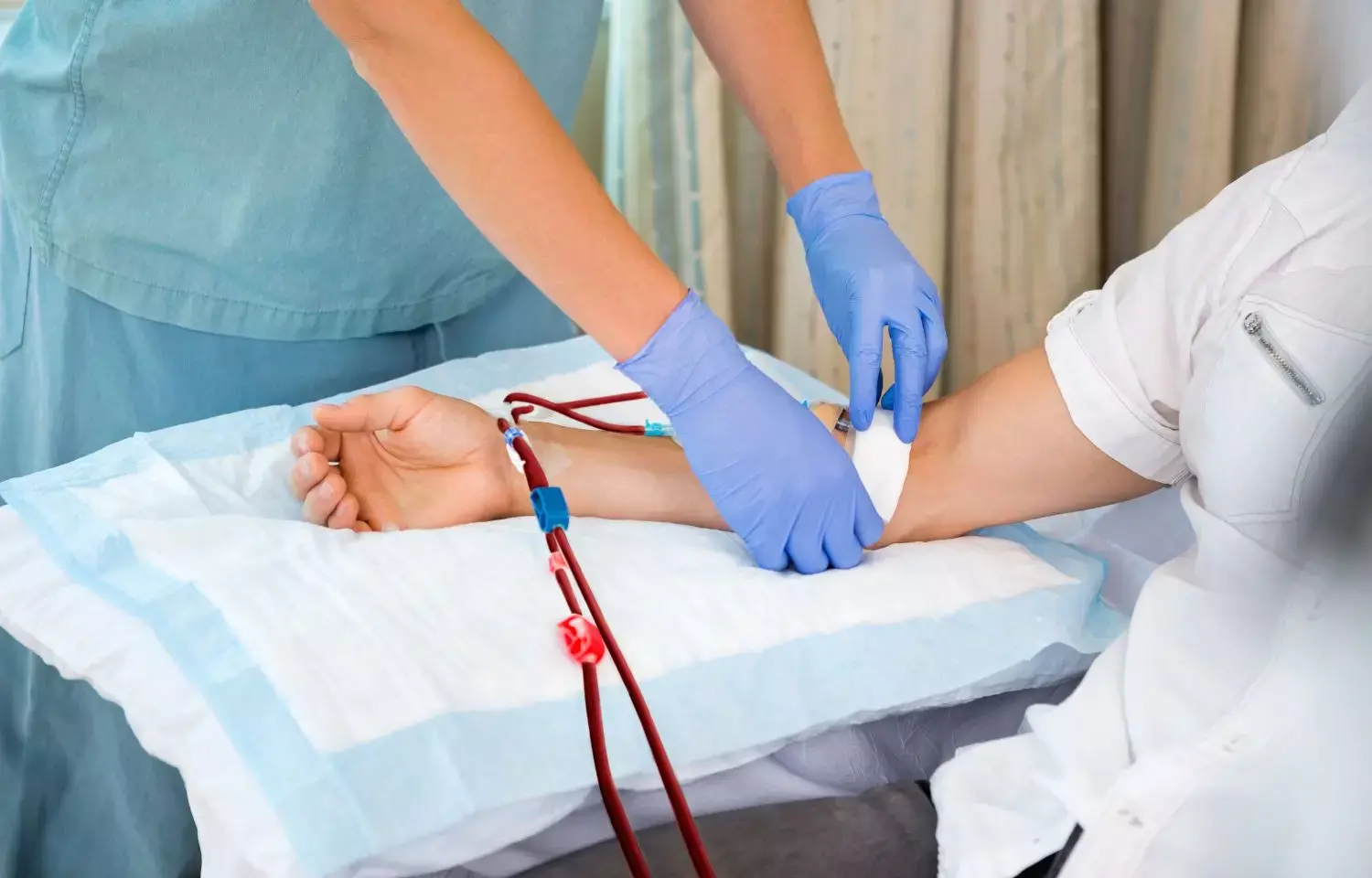
Patients with kidney failure undergoing chronic hemodialysis (HD) often grapple with imbalances in mineral metabolism and disruptions in cardiovascular and skeletal health, contributing to a higher mortality rate. However, a recent study conducted in an HD center in Iran suggests that intradialytic exercise could be a game-changer in regulating these abnormalities and improving patient well-being.
The randomized controlled trial, which spanned 6 months, divided 44 adult patients receiving chronic HD into two groups: an intervention group, where participants engaged in 60 minutes of intradialytic exercise during the second hour of their thrice-weekly dialysis sessions, and a control group that did not partake in any intradialytic exercise.
The primary focus of the study was on critical markers of mineral metabolism, including serum calcium, serum phosphorous, and parathyroid hormone levels. Secondary outcomes examined were serum alkaline phosphatase and the calcium-phosphorous product.
The findings of the study yielded promising results. Over the 6-month intervention period, significant differences emerged between the two groups across all primary and secondary outcomes. Notably, participants in the intradialytic exercise group experienced a statistically significant increase in serum calcium levels, while seeing significant decreases in serum phosphorous, parathyroid hormone, alkaline phosphatase, and the calcium-phosphorous product.
These results suggest that incorporating intradialytic exercise routines, lasting at least 60 minutes during thrice-weekly dialysis sessions, can positively impact bone mineral metabolism in adult patients undergoing HD. This is a significant development, as disruptions in mineral metabolism are known to contribute to the high mortality rate observed in these patients.
While these findings are promising, researchers emphasize the need for further studies to delve into the effects of different types of exercise on bone mineral disorders and all-cause mortality among HD patients. This study opens up new avenues for improving the health and quality of life of individuals facing the challenges of chronic kidney disease and hemodialysis.
Reference:
Tabibi, M. A., Wilund, K. R., Salimian, N., Nikbakht, S., Soleymany, M., Roshanaeian, Z., Nazemi, F., & Ahmadi, S. (2023). The effect of intradialytic exercise on calcium, phosphorus and parathyroid hormone: a randomized controlled trial. In BMC Nephrology (Vol. 24, Issue 1). Springer Science and Business Media LLC. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-023-03327-7
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


