- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
intradialytic exercise regime is safe and effective in hemodialysis patients: Study
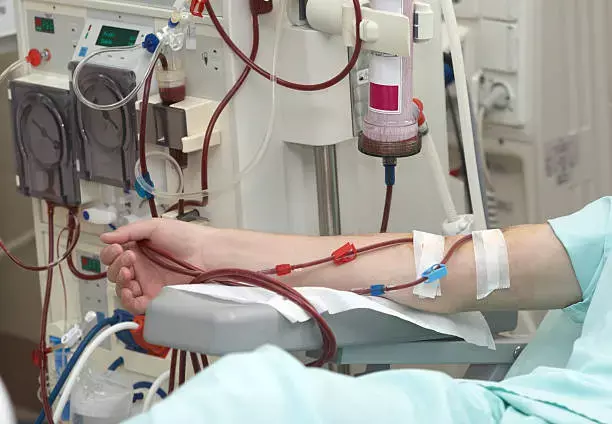
Patients over 70 years old with Chronic kidney disease (CKD) had higher Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB) scores after 6 months of intradialytic exercise therapy, compared to patients without exercise therapy, according to a recent study published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
Exercise is fundamentally important in managing chronic diseases and improving health-related quality of life (HRQL). However, whether intradialytic exercise is safe through assessment of changes in dialytic parameters and has a positive impact on health-related quality of life (HRQL) and depression status of hemodialysis patients requires further research with diverse racial and cultural populations to identify.
A group of researchers from Taiwan conducted a study to evaluate the effects of intradialytic exercise on dialytic parameters, health-related quality of life (HRQL), and depression status in hemodialysis patients. A randomized controlled trial was conducted at a medical center in Northern Taiwan. Sixty-four hemodialysis patients were recruited using stratified random sampling. Participants were randomized into an experimental group (EG) (EG, n = 32) or a control group (CG) (CG, n = 32). The experimental group (EG) received a 12-week intradialytic exercise program while the control group (CG) maintained their usual lifestyles. Dialytic parameters, health-related quality of life (HRQL), and depression status were collected at baseline and at 12 weeks.
The results of the study are as follows:
No differences in the dialytic parameters from the baseline between both groups.
However, the experimental group (EG) had increased health-related quality of life (HRQL) (ß = 22.6, p < 0.001) and reduced depression status (ß = −7.5, p = 0.02) at 12 weeks compared to the control group (CG). Therefore, the researchers concluded that a 12-week intradialytic exercise regime is safe and effective in improving health-related quality of life (HRQL) and reducing depression status for hemodialysis patients.
Reference:
Effects of Intradialytic Exercise on Dialytic Parameters, Health-Related Quality of Life, and Depression Status in Hemodialysis Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial by Chia-Huei Lin et al. published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
doi: 10.3390/ijerph18179205
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


