- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Magnetic hydrogel may facilitate efficient removal of kidney stones: Study
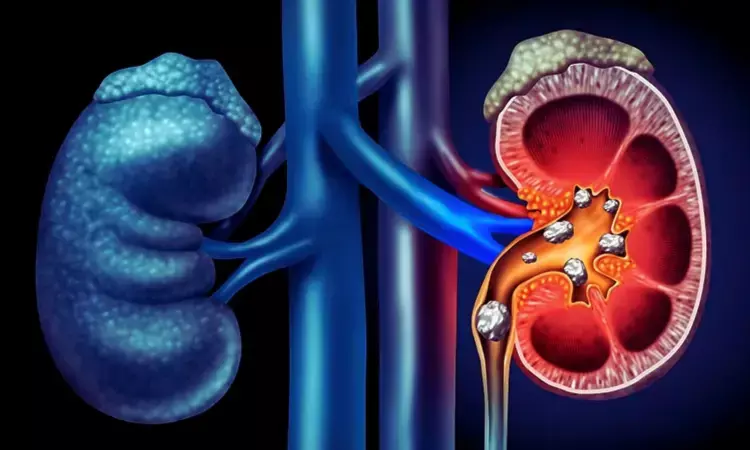
USA: A recent study published in Nature Communications has shed light on the utility of magnetic hydrogel for the efficient retrieval of kidney stone fragments during ureteroscopy.
About one in nine individuals are affected by kidney stones, causing intense pain and severe infections. They pose a significant health burden, with over 1.3 million emergency room visits and healthcare expenditures exceeding $5 billion annually in the US. The most common treatment is laser fragmentation through ureteroscopy, but success rates in stone elimination range from 60% to 75%. Small, hard-to-extract fragments are often left behind, risking natural elimination. Technologies like fragment adhesion with biopolymers, focused ultrasound, and negative pressure aspiration have been explored, but they have limitations, especially with standard ureteroscope channel sizes.
The study introduced the Magnetic System for Total Nephrolith Extraction, a system designed to enhance the efficiency of renal calculus fragment removal. In this system, the stones are coated with a magnetic hydrogel and retrieved using a magnetic guidewire compatible with standard ureteroscopes.
In vitro, the separation of laser-obtained renal calculus fragments was done by size and coated either with ferumoxytol alone or combined with chitosan (Hydrogel CF). Then, the treated fragments were subjected to a magnetic wire for fragment removal assessment.
Additional tests included scanning electron microscopy and cell culture with human urothelial cells to assess the cytotoxicity of the magnetic hydrogel components. The hydrogel and its components underwent efficacy and safety evaluations in in-vitro studies, murine models, and human tissue samples to assess their impact on urothelium and antibacterial properties.
The Hydrogel CF comprising chitosan and ferumoxytol showed 100% effectiveness in eliminating all tested fragments, even those measuring up to 4 mm, across various stone compositions. Particle tracing simulations indicated that small-sized stones measuring 1 and 3 mm could be captured several millimetres away. The binding of ferumoxytol and Hydrogel CF to the surface of calcium oxalate stones was confirmed by scanning electron microscopy.
Even after a 4-hour exposure, Hydrogel CF components did not induce significant cytotoxicity on human urothelial cells. Moreover, live mouse studies revealed that Hydrogel CF caused less bladder urothelium exfoliation compared with chitosan, and the urothelium returned to normal within 12 hours. In addition, these components exhibited antibacterial properties, inhibiting the growth of uropathogenic bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis, comparable to that of ciprofloxacin.
The ability to eliminate lithiasic fragments, the absence of significant urothelial toxicity, and antibacterial activity indicate that magnetic hydrogel use could be integrated into laser treatments for renal stones through ureteroscopy without immediate complications.
"By enabling the efficient retrieval of kidney stone fragments, our method can lead to improved patient outcomes and stone-free rates," the research team wrote.
"The antibacterial properties could offer potential postoperative benefits while decreasing procedural time," they concluded. "Further animal studies are underway to assess Hydrogel CF's safety before proceeding to human clinical trials."
Reference:
Ge, T. J., Roquero, D. M., Holton, G. H., Mach, K. E., Prado, K., Lau, H., Jensen, K., Chang, T. C., Conti, S., Sheth, K., Wang, S. X., & Liao, J. C. (2023). A magnetic hydrogel for the efficient retrieval of kidney stone fragments during ureteroscopy. Nature Communications, 14(1), 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-38936-1
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


