- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Retzius-Sparing Robot-Assisted Surgery Enhances Urinary Function and Quality of Life in Prostate Cancer Patients: Study
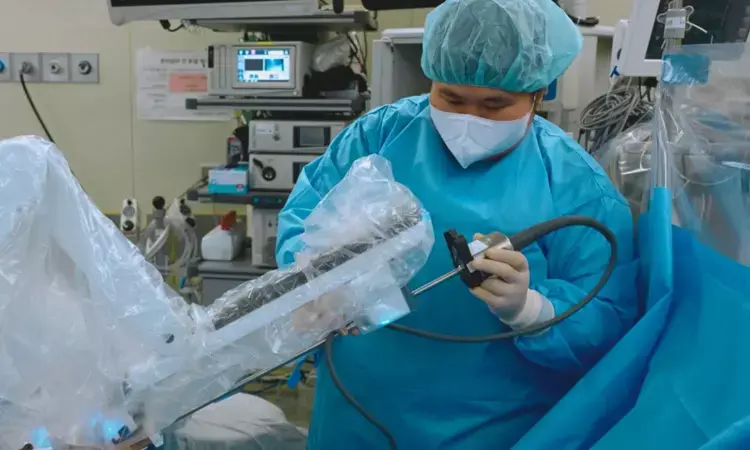
Belgium: A recent study comparing Retzius-sparing robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy (rsRALP) with standard robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy (sRALP) has yielded promising results, particularly in terms of urinary function and overall quality of life (QoL) for patients undergoing the procedure. The study followed patients over two years, focusing on patient-reported outcomes and oncological assessments.
The study, published in The Prostate Journal, showed that the rsRALP technique notably enhances both early and short-term urinary function and quality of life compared to sRALP. Although it is linked to less favorable characteristics regarding positive surgical margins (PSM), there was no significant decline in biochemical recurrence-free survival (BCR-free survival) observed with rsRALP.
As prostate cancer remains one of the most common cancers affecting men, advancements in surgical techniques are crucial. Considering this, Romain Diamand, Université Libre de Bruxelles, Brussels, Belgium, and colleagues aimed to assess the two-year functional and oncological outcomes of Retzius-sparing robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy (rsRALP) compared to the standard approach (sRALP).
For this purpose, the researchers identified a total of 200 consecutive patients who underwent either sRALP (n = 100) or rsRALP (n = 100) for clinically localized prostate cancer at a single referral center in Europe between 2015 and 2020. This data was collected from a prospective cohort as part of the Belgian Cancer Registry.
The primary outcomes focused on functional results and QoL, evaluated using validated patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) at 1, 3, 12, and 24 months following surgery. Secondary outcomes included oncological results, specifically PSM and five-year biochemical recurrence (BCR) rates. The researchers employed Kaplan-Meier analysis with log-rank tests and multivariable Cox regression for their statistical evaluation.
The study led to the following findings:
- The median follow-up period was 60 months, and there were no significant differences between the two surgical approaches regarding patient and tumor characteristics.
- Patients who underwent Retzius-sparing robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy reported significantly better urinary function and quality of life at all follow-up intervals. However, sexual function did not show a significant difference 12 months post-surgery.
- There was no notable difference in the rate of positive surgical margins between the two approaches (31% for rsRALP versus 32% for sRALP).
- rsRALP was associated with longer positive surgical margins (5 mm versus 2.5 mm), a higher rate of multifocality (34% versus 13%), and a greater occurrence of organ-confined disease (59% versus 39%), as well as more cases at anterior locations (37% versus 16%).
- Five-year biochemical recurrence-free survival did not differ significantly between the groups, and the surgical approach was not found to be a predictor of biochemical recurrence.
As prostate cancer remains one of the most common cancers affecting men, advancements in surgical techniques are crucial. The study's results offer valuable insights for clinicians and patients, encouraging a more personalized approach to prostate cancer treatment.
"The findings from this study may help shape future practices in the management of prostate cancer, enhancing patient care and outcomes," the researchers concluded.
Reference:
Diamand, R., Bernard, L., Mjaess, G., Benijts, J., Assenmacher, C., & Assenmacher, G. Retzius-sparing versus standard robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy: A two-year patient-reported and oncological assessment. The Prostate. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.24807
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


