- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Sarcopenia prevalence high among hemodialysis patients, quadriceps muscle ultrasound may detect
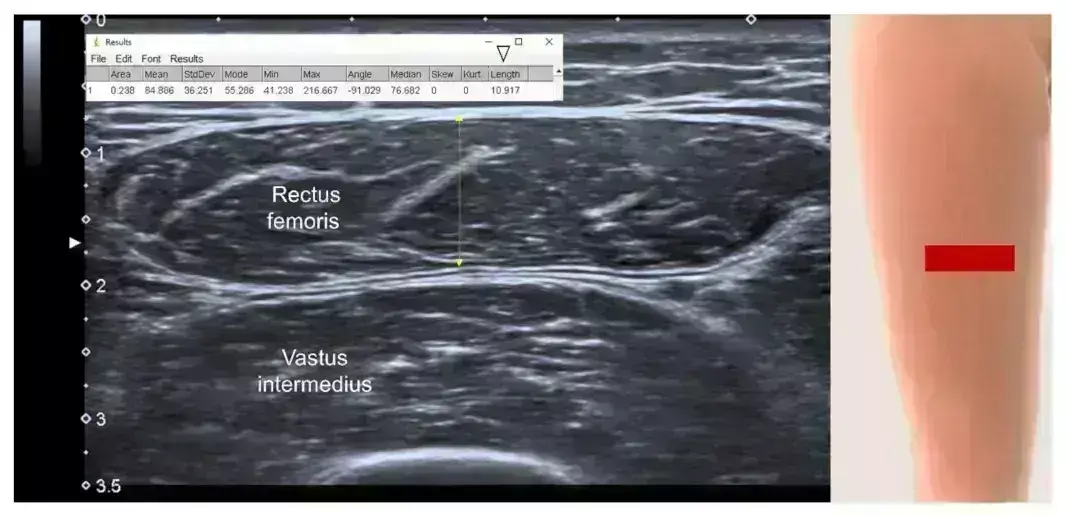
Sarcopenia prevalence is high among hemodialysis patients, and quadriceps muscle ultrasound may detect suggests a new study published in the BMC Nephrology.
Sarcopenia is a common problem in hemodialysis (HD) patients, and it is diagnosed by low muscle mass, strength and/or low physical performance. Muscle ultrasound (US) is a non-invasive portable tool that might be used for the assessment of muscle mass. The current study aimed to investigate the concordance between muscle US and bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) in the diagnosis of sarcopenia in hemodialysis patients. This cross-sectional study included 41 hemodialysis patients. Sarcopenia was diagnosed according to the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People (EWGSOP). The skeletal mass index was measured by BIA and the muscle strength was measured by handgrip strength. Muscle ultrasound was used to measure the cross-sectional area (CSA) and thickness of the quadriceps and biceps muscles. Results: The current study included 41 patients on hemodialysis (25 males), with a mean (SD) age of 44.18 (13.11) years and a median hemodialysis duration of 48 months. Sarcopenia was diagnosed in 58.5% of the patients. Patients with sarcopenia had significantly lower quadriceps muscle CSA than those without sarcopenia. The optimal cut-offs of quadriceps muscle cross-sectional area for both males and females for the diagnosis of sarcopenia were 2.96 and 2.92 cm2, respectively. Sarcopenia is prevalent among Egyptian hemodialysis patients. Muscle ultrasound on the quadriceps muscle cross-sectional area could be used for the diagnosis of sarcopenia in these patients.
Reference:
Nagy, E., Samaan, E., El-Gamal, M. et al. Concordance between muscle mass assessed by bioelectrical impedance analysis and by muscle ultrasound: a cross-sectional study in a cohort of patients on chronic hemodialysis. BMC Nephrol 25, 49 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-024-03487-0
Keywords:
Sarcopenia, prevalence, hemodialysis patients, quadriceps, muscle ultrasound, detect, BMC Nephrology, Nagy, E., Samaan, E., El-Gamal, M, Chronic kidney disease
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


