- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Trazadone and CBT no more effective than placebo for improving insomnia among long-term dialysis patients
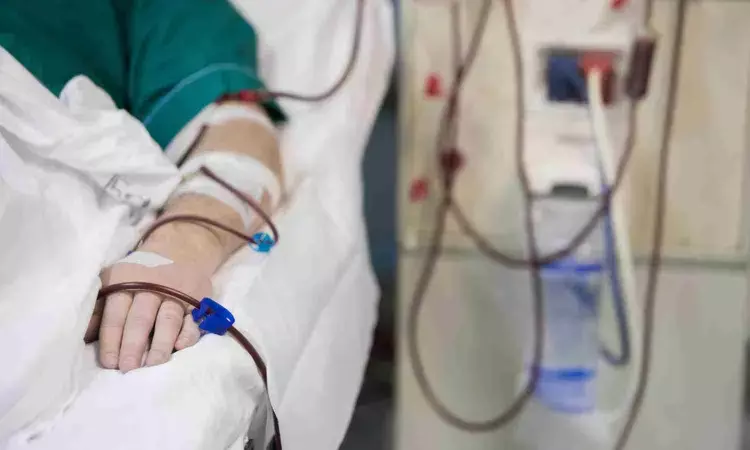
Dialysis Unit at Silchar Medical College Vandalised, Services Disrupted
A clinical trial of more than 120 persons undergoing hemodialysis found that cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) or trazodone were no more effective than placebo for improving mild to moderate chronic insomnia. These findings are important given the prevalence of insomnia among long-term dialysis patients. The study is published in Annals of Internal Medicine.
Insomnia affects up to 50 percent of persons undergoing long-term dialysis. Because insomnia is associated with exacerbated fatigue, depression, pain perception, and poor quality of life, patients
place a high priority on finding effective treatments for this condition. CBT-I and trazodone are commonly used interventions to treat insomnia in the general population, but evidence for efficacy and safety of insomnia treatments cannot be extrapolated to persons undergoing long-term dialysis.
A team led by researchers from the University of Washington randomly assigned 126 persons undergoing hemodialysis and experiencing chronic insomnia to 6 weeks of CBT-I, trazadone, or placebo to compare the effectiveness of the interventions. Participants were assessed for severity of insomnia at 7 and 25 weeks using the Insomnia Severity Index (ISI) questionnaire. The authors found that the change in ISI scores were the same for patients regardless of the intervention used, but serious adverse events occurred more frequently in participants using trazodone. According to the authors, given the high burden of insomnia in dialysis patients and high priority placed by patients for symptom relief, more trials are needed to investigate additional therapies for this condition.
An accompanying editorial by Ronald B. Postuma, MD, MSc highlights how the different causes of insomnia impact its treatment. The author notes that lack of efficacy observed with CBT-I in this study is remarkable, given the extremely strong evidence base for its utility in primary insomnia, suggesting that the typical psychophysiological drivers of insomnia in the general population may be simply less pertinent in hemodialysis patients. The authors also highlights that future studies should explore medications specifically designed for insomnia and treatments that target restless legs and neuropathic pain.
Reference:
Rajnish Mehrotra, Daniel Cukor, Susan M. McCurry, Tessa Rue, Effectiveness of Existing Insomnia Therapies for Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis, Annals of Internal Medicine, https://doi.org/10.7326/M23-1794.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


