- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Artificial intelligence may help in faster detection of ischemic stroke
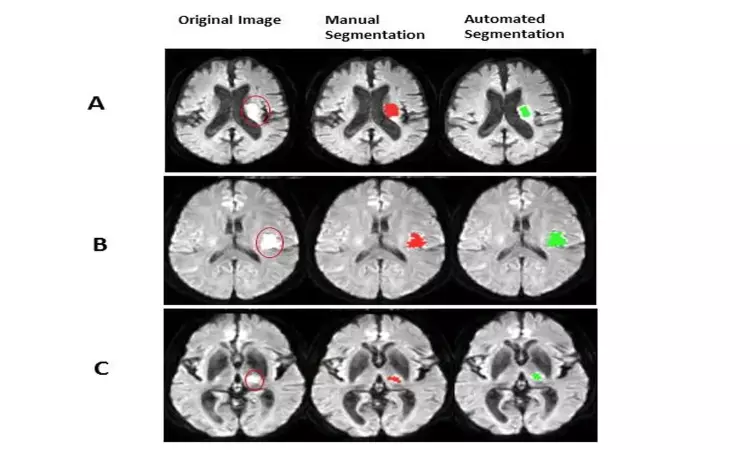
Researchers have introduced a new fully automated technique for detection of acute ischemic stroke on MRI with help of artificial intelligence.The results of the study have been published in the Journal of Neuroscience Methods.
Timely detection and accurate segmentation of acute ischemic stroke (AIS) lesions on magnetic resonance images (MRIs) are essential for the triaging patient for endovascular therapy. Lesion segmentation is a routine process where the abnormal areas within brain images are qualitatively and manually picked by expert radiologists. However, manual lesion segmentation is time consuming and suffers from operator-bias. Accordingly, efficient and low-cost approaches for AIS lesion screening are yet to be introduced.
This research introduces a novel and fully automated technique for detection and segmentation of AIS lesions on MRIs and classification of images into stroke and non-stroke. This fully automated anomaly-detection method compares diffusion weighted images (DWIs) and apparent diffusion coefficients (ADC) images of the subjects with a group of healthy images in voxel-level. Areas with hyperintensity on DWI and hypointensity on ADC are identified as lesions and saved as lesion masks. The lesion segmentation method was investigated on approximately 100 cases. Since there is a risk of false lesion identification due to the artifacts, noises, and image low resolution, the lesion masks created by the method are screened and filtered via a binary classifier which either confirms that the created lesion mask contains a real AIS lesion or not. The classification performance was evaluated on about 200 MRIs.
The published results in the Journal of Neuroscience Methods show good agreement with the manually drawn lesions by experts (gold standard). The whole approach, including lesion segmentation and image classification, is straightforward, fast and does not require high computation power and memory.
"We believe that this method has the capacity to be implemented on an ordinary desktop workstation integrated into the routine clinical diagnostic pipelines of the hospitals. This approach can help the radiologists to speed up the workflow of lesion detection and to reduce the operator bias in lesion segmentation owing to the reproducibility of the method", tells project researcher Sanaz Nazari-Farsani from Turku PET Centre.
for further references log on to:
Medical Dialogues Bureau consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


