- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Carotid atherosclerotic plaque microcalcification independently associated with recurrent neurovascular events reveals pilot study
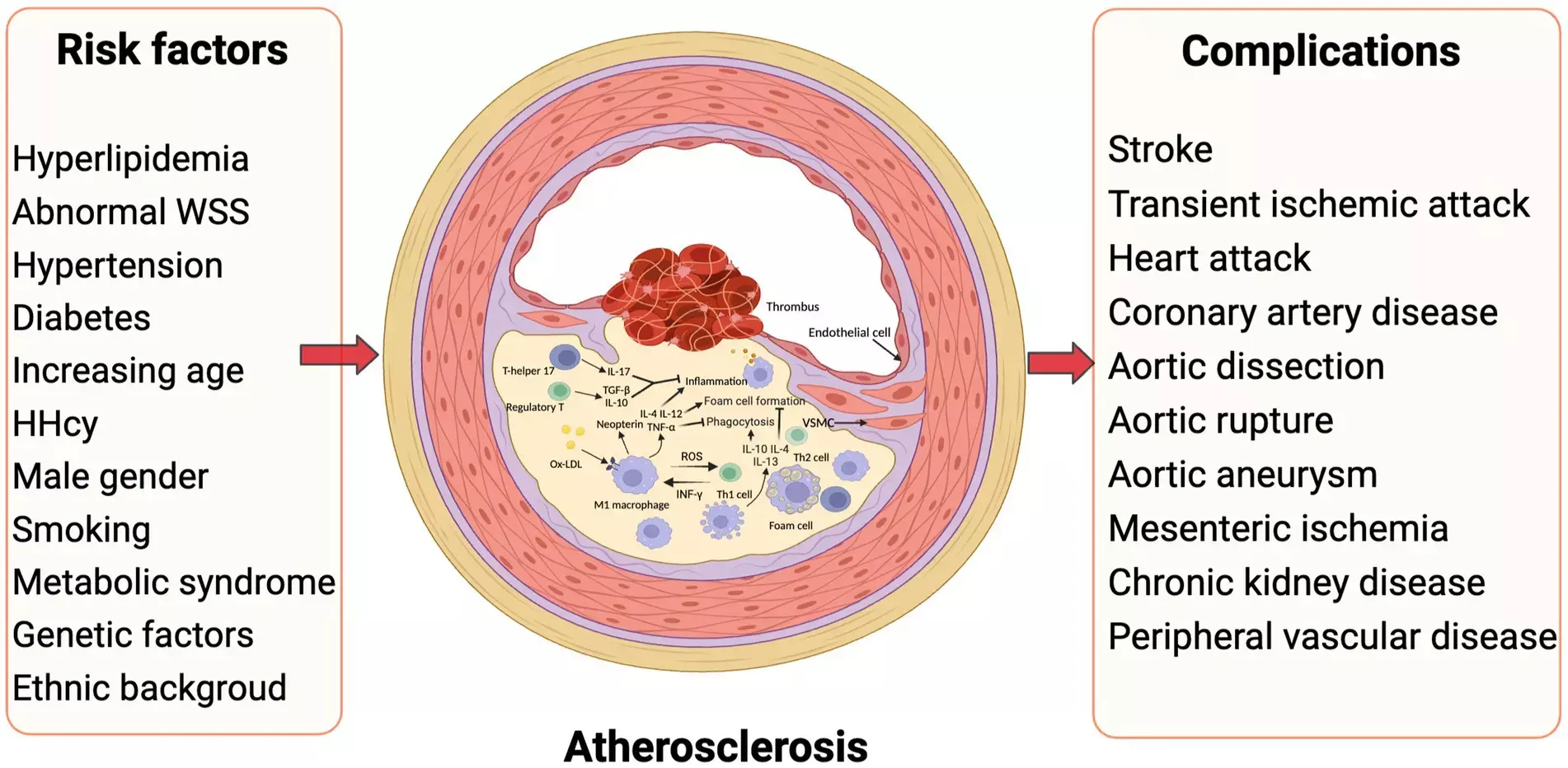
Carotid atherosclerotic plaque microcalcification independently associated with recurrent neurovascular events reveals a pilot study published in the International Journal of Stroke.
Microcalcification and macrocalcification are critical processes in atherosclerotic plaque progression, though how these processes relate to the risk of stroke recurrence in symptomatic carotid atherosclerosis is poorly understood. They performed a post-hoc analysis of data from the ICARUSS study, where individuals with acute ischemic stroke originating from ipsilateral carotid stenosis of ≥50% underwent 18F-sodium fluoride-positron emission tomography (NaF-PET) to measure microcalcification. Tracer uptake was quantified using maximum tissue-to-background ratio (TBRmax). Macrocalcification was measured on computed tomography (CT) using Agatston scoring. Patients were followed up for six months for recurrent ipsilateral neurovascular events. Results: Five (27.8%) of 18 individuals had a recurrent ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack.
Ipsilateral carotid plaque NaF uptake at baseline was higher in those with recurrent events compared to those without, and this association remained after adjustment for other vascular risk factors (OR 1.24, 1.03-1.50). Macrocalcification score in the symptomatic artery was also significantly independently associated with ipsilateral recurrence, but the effect size was relatively smaller (OR 1.12, 1.06-1.17 for each 100 unit increase). The findings indicate that microcalcification in symptomatic carotid plaques is independently associated with ipsilateral ischemic stroke recurrence. Furthermore, differences in the extent of active microcalcification in macrocalcified plaques may help explain variation in the relationship between calcified carotid plaques and stroke recurrence reported in the literature. Our pilot study indicates that evaluation of carotid artery microcalcification using NaF-PET may be a useful method for risk-stratification of carotid atherosclerosis, though our findings require confirmation in larger cohorts
Reference:
Bhakta S, Tarkin J, Chowdhury M, Rudd J, Warburton EA, Evans NR. Carotid atherosclerotic plaque microcalcification is independently associated with recurrent neurovascular events: a pilot study. International Journal of Stroke. 2024;0(ja). doi:10.1177/17474930241264734
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


