- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Limiting hematoma growth may improve mortality in anticoagulant-related intracerebral haemorrhage patients: Study
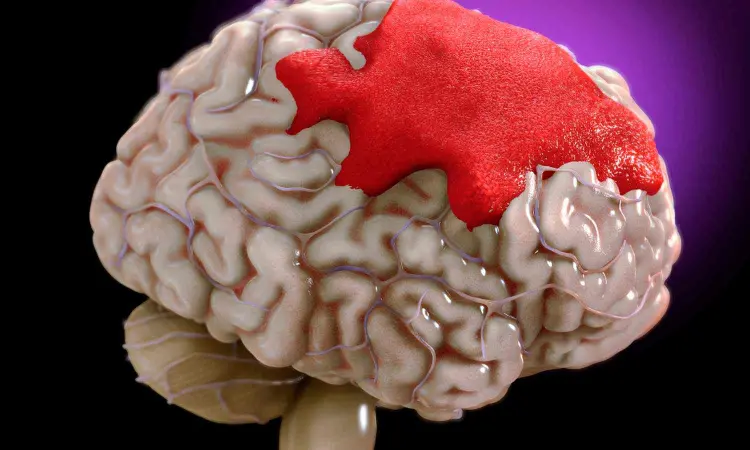
A secondary analysis of ANNEXa-I, presented today at the European Stroke Organisation Conference (ESOC) 2024, showed the clinical consequences of hematoma growth and of the less commonly occurring thromboembolic events. Data pooled from both treatment arms of ANNEXa-I demonstrated that hematoma expansion and thromboembolic events are independently associated with 30-day mortality. Hematoma expansion was also associated with poor functional outcomes 30 days post-event.
The ANNEXa-I trial investigated the effect of a new reversal agent (Andexanet alfa) in the treatment of oral Factor Xa (FXa) inhibitor in patients experiencing an intracerebral haemorrhage (ICH) versus usual care. The drug was shown to reduce the occurrence of hematoma growth, but also resulted in more thromboembolic events than in the standard of care group.
In this secondary analysis the authors used a time-dependent regression analysis combining the data from both trial arms and found that the occurrence of hematoma growth and of thromboembolic events were associated with increased 30-day mortality with a Hazard Ratio of 2.98 and 3.33, respectively.
In a second analysis using a landmark approach, which included all events of haematoma expansion and thromboembolic events across both trial arms occurring up to day 5, haematoma expansion was significantly associated with worse functional outcome. There was no association between thromboembolic events and functional outcome, but the interpretation of this result is limited given the low event rate of thromboembolic complications in the first 5 days. Overall, haematoma expansion was four times more frequent than thromboembolic complications.
Professor David Seiffge, one of the lead authors of the study from Bern, Switzerland commented, “One in three anticoagulant-related intracerebral haemorrhage patients will experience haematoma expansion, which is in turn associated with a three-fold increase in mortality and survivors suffer from significant disability. This new analysis demonstrates that prevention of haematoma expansion is a priority for treatment of these patients, and will help to support clinicians in their benefit/risk analysis.”
ICH, a subtype of stroke, accounts for 10-15% of strokes across Europe, but is responsible for half of the stroke-related morbidity and mortality. Advancements in treatment have been slower than for ischemic stroke. Anticoagulant-related ICH becomes increasingly common with increasing prescription of anticoagulants drugs in the community. Factor Xa inhibitors, the most prescribed anticoagulant type, has up to now been lacking an effective antidote. A drug that convincingly prevents hematoma expansion is a breakthrough for anticoagulant- related ICH treatment. A downside of the treatment is the increased risk of thromboembolic complications, the clinical consequences of which were previously unknown.
Reference:
CLINICAL CONSEQUENCES OF HAEMATOMA EXPANSION AND THROMBOEMBOLIC EVENTS IN PATIENTS WITH FACTOR XA-INHIBITOR ASSOCIATED ICH IN ANNEXA-I. Presented at the European Stroke Organisation Conference; 15 May 2024; Basel, Switzerland.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


