- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Portable fundus photography more accurate than smartphone fundoscopy for neurological examination: Study
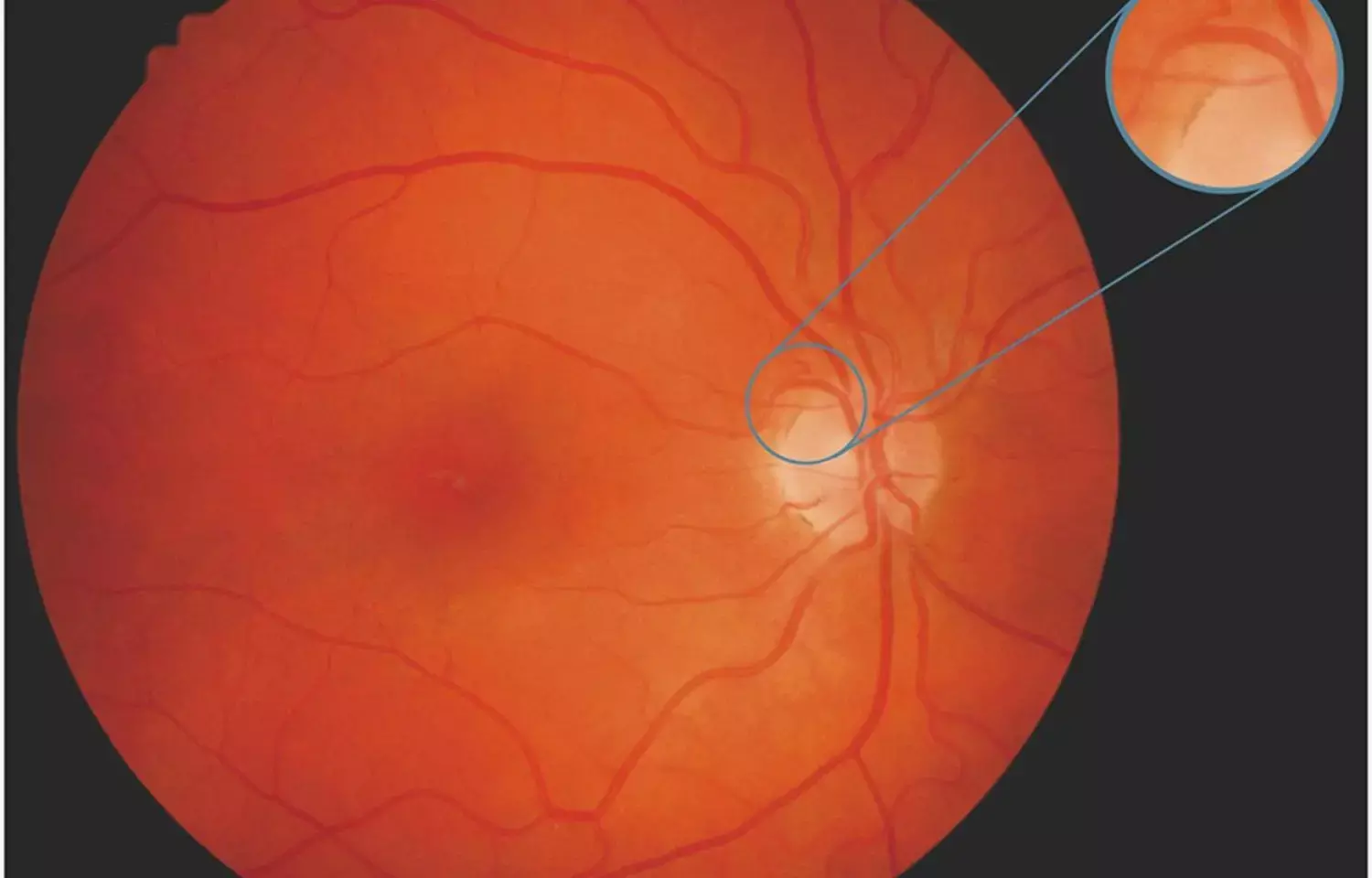
Australia: Portable non-mydriatic fundus photography (NMFP) screening seems more accurate than smartphone fundoscopy (SF). Both are feasible and well tolerated by patients and are diagnostically superior to routine fundoscopic practice. These are results from a recent study published in the European Journal of Neurology.
The researchers wrote in their study, "our study demonstrates a high prevalence of fundus pathology in neurology inpatients which was missed by the present fundoscopy practices."
Fundoscopy although a critical part of the neurological examination, is under-utilized, challenging, and unreliable performed. Hamish P. Dunn, University of Sydney, Faculty of Medicine and Health, Sydney, NSW, Australia, and colleagues, therefore, aimed to determine the prevalence of fundus pathology in neurology inpatients in prospective cross-sectional surveillance and diagnostic accuracy study. They also compared the diagnostic accuracy of current fundoscopy practice with systematic screening with smartphone fundoscopy and portable non-mydriatic fundus photography.
The study included adult patients admitted under neurology in an Australian hospital. Inpatients were randomized to initial NMFP (RetinaVue 100, Welch Allyn) or SF (D-EYE) followed by a crossover to the alternative modality.
Grading of images was done by neurology doctors, using telemedicine consensus neuro-ophthalmology NMFP grading as the reference standard. Feasibility parameters included comfort, ease, and speed.
Based on the study, the researchers found the following:
- Of 79 enrolled patients, 14.1% had neurologically relevant pathology (seven, disc pallor; one, hypertensive retinopathy; three, disc swelling).
- The neurology team performed direct ophthalmoscopy in 6.6% of cases and missed all abnormalities.
- SF had a sensitivity of 30%–40% compared with NMFP (45.5%); however, it had a lower rate of screening failure (1% vs. 13%), a shorter examination time (1.10 vs. 2.25 min), and a slightly higher patient comfort rating (9.2 vs. 8/10).
"Our study found a high prevalence of fundus pathology amongst neurology inpatients. This pathology was missed by standard direct ophthalmoscope (DO) techniques," the researchers wrote.
"Portable NMFP screening appears more accurate than SF, both are, however, diagnostically superior to routine fundoscopic practice, well tolerated by patients, and can feasibly be incorporated into routine neurology inpatient care," they concluded.
Reference:
He G, Dunn HP, Ahmad KE, Watson E, Henderson A, Tynan D, Leaney J, White AJ, Hewitt AW, Fraser CL. Fundoscopy use in neurology departments and the utility of smartphone photography: a prospective prevalence and crossover diagnostic accuracy study amongst neurology inpatients. Eur J Neurol. 2022 May 9. doi: 10.1111/ene.15390. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35531644.
direct ophthalmoscopy (DO)
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


