- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Preoperative Oedema Strongly Linked to Seizure Risk in Meningioma Patients: Meta-Analysis Findings
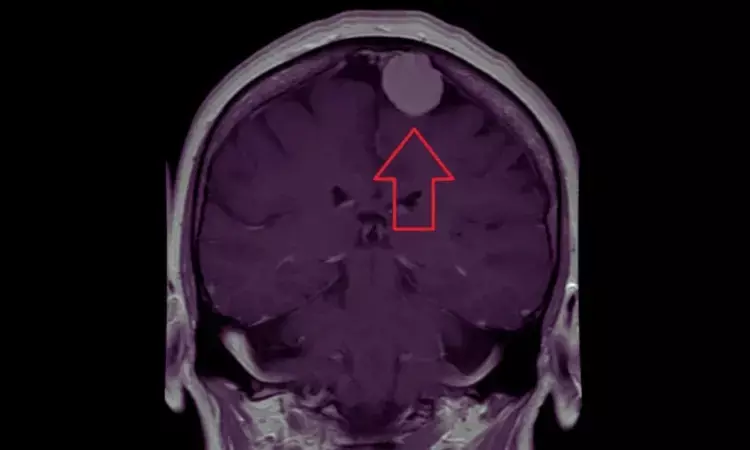
UK: A recent systematic review and meta-analysis published in Neurosurgical Review shed light on the significant role of preoperative oedema in predicting seizure risk in patients with meningioma. The meta-analysis revealed that preoperative oedema substantially increased the likelihood of seizures in meningioma patients.
"Those with oedema had 3.5 times higher odds of experiencing preoperative seizures (OR: 3.5) and faced an elevated risk of both early (OR: 1.5) and late (OR: 1.9) postoperative seizures. These findings highlight the importance of assessing seizure risk in patients with oedema, particularly in the preoperative stage," the researchers reported.
The researchers note that meningiomas, though benign intracranial tumors are often associated with complications such as seizures and oedema. Understanding the factors contributing to seizure risk is crucial for clinicians and patients in the meningioma community. While numerous studies have explored the relationship between oedema and seizures, their conclusions remain inconsistent. Additionally, existing meta-analyses have largely overlooked oedema as a key prognostic factor.
To bridge this gap, Matthew J. Tanti, Department of Neurology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Leeds, LS1 3EX, UK, and colleagues aimed to comprehensively review and summarize the available literature on the role of oedema in predicting seizure occurrence in meningioma patients.
For this purpose, the researchers conducted a comprehensive search across multiple databases, including OVID, Scopus, PubMed, Web of Science, ClinicalTrials.gov, and Google Scholar, up to April 2024, selecting studies with more than 10 human meningioma participants. Statistical analyses were performed using R-Studio, adhering to the Cochrane and Campbell guidelines for systematic reviews and meta-analyses. The risk of bias was evaluated using ROBINS-E, and the study protocol was registered on INPLASY.
Fifty-one studies were included in the meta-analysis, while 21 were considered for narrative review. Most studies focused on surgically treated adult patients, and after excluding outliers, heterogeneity was found to be low.
Key Findings:
- Preoperative oedema was associated with preoperative seizure (k = 28, n = 7,725, OR 3.5), early postoperative seizure (k = 9, n = 2,929, OR 1.5) and late postoperative seizure (k = 9, n = 2,150, OR 1.9).
- An additional adjusted analysis was performed for preoperative seizures, which was also significant (k = 3, n = 2,241, OR 3.9).
- There were few studies of post-radiosurgery oedema and seizure and of postoperative oedema and seizure, with insignificant but positive associations.
The findings highlight preoperative oedema as a significant adverse prognostic factor for the development of preoperative seizures in meningioma patients. While preoperative oedema was associated with a modestly increased risk of early and late postoperative seizures, other factors may have a more substantial influence on postoperative seizure occurrence.
The researchers found no study-level characteristics that significantly modified the risk of pre- or postoperative seizures due to oedema. Notably, this is also the first meta-analysis to investigate seizure risk associated with post-radiosurgery oedema, revealing a positive but statistically insignificant association.
"These findings emphasize the need for further research to clarify the role of oedema in seizure outcomes and guide clinical management in meningioma patients," they concluded.
Reference:
Tanti, M.J., Nevitt, S., Yeo, M. et al. Oedema as a prognostic factor for seizures in meningioma - a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg Rev 48, 249 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-025-03416-1
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


