- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Sleep Apnea associated with diminished cognition and altered white matter integrity: JAMA
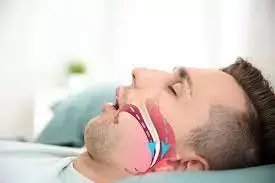
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is associated with diminished cognition and altered white matter integrity (compared with no OSA) in middle to late adulthood according to a recent study published in the JAMA Network Open.
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is associated with cognitive impairment and brain structural alterations, but longitudinal outcomes are understudied.
A Study was conducted to examine the associations of OSA with cognition and white matter (WM) integrity over a 4-year period.
This prospective cohort study was conducted in a community-based adult population among participants who had both baseline (2011-2014) and 4-year follow-up (2015-2018) polysomnography, diffusion tensor imaging, and cognitive assessment data. Participants with neurological disorders, anomalous findings on brain magnetic resonance imaging, or inadequate quality of the evaluations were excluded. Data were analyzed from March to November 2021.
The main outcomes were proportional changes over a 4-year period in neuropsychological performance and WM integrity. The neuropsychological assessment battery included verbal and visual memory, verbal fluency, Digit Symbol-coding, Trail Making Test-A, and Stroop Test. WM integrity was assessed by fractional anisotropy, axial, and radial diffusivity. To examine interactions with age and sex, participants were subgrouped by age older than 60 years vs 60 years or younger and men vs women.
Results:
- A total of 1998 individuals were assessed for eligibility, and 888 were excluded based on exclusion criteria, leaving 1110 participants for analysis, including 458 participants grouped as OSA-free, 72 participants with resolved OSA, 163 participants with incident OSA, and 417 participants with persistent OSA.
- Incident OSA was associated with altered WM integrity and with concomitant changes in sustained attention compared with participants without OSA
- Participants with resolved OSA showed better visual recall at the follow-up with concordant changes in diffusion parameters at the relevant anatomic areas. In the older group only (age >60 years), persistent OSA was associated with altered WM integrity and cognition.
- Sex also was associated with modifying the association of OSA with WM integrity of the left posterior internal capsule, the left genu of corpus callosum, and the right middle cerebellar peduncle only in men and with cognition only in women
These findings suggest that dynamic changes in OSA status were significantly associated with WM integrity and cognition, which varied by age and sex. It is possible that adequate interventions for OSA could better preserve brain health in middle to late adulthood.
Reference:
Lee MH, Lee SK, Kim S, Kim REY, Nam HR, Siddiquee AT, Thomas RJ, Hwang I, Yoon JE, Yun CH, Shin C. Association of Obstructive Sleep Apnea With White Matter Integrity and Cognitive Performance Over a 4-Year Period in Middle to Late Adulthood. JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Jul 1;5(7):e2222999. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.22999. PMID: 35857321.
Keywords:
Obstructive sleep apnea, white matter integrity, middle, late adulthood, JAMA Netw Open, Min-Hee Lee, Seung Ku Lee, Soriul Kim, Regina E Y Kim, Hye Ryeong Nam, Ali T Siddiquee , Robert J Thomas, Inha Hwang, Jee-Eun Yoon, Chang-Ho Yun, Chol Shin
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


