- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Tenecteplase fails to improve functional outcomes in wake-up stroke patients selected using non-contrast CT
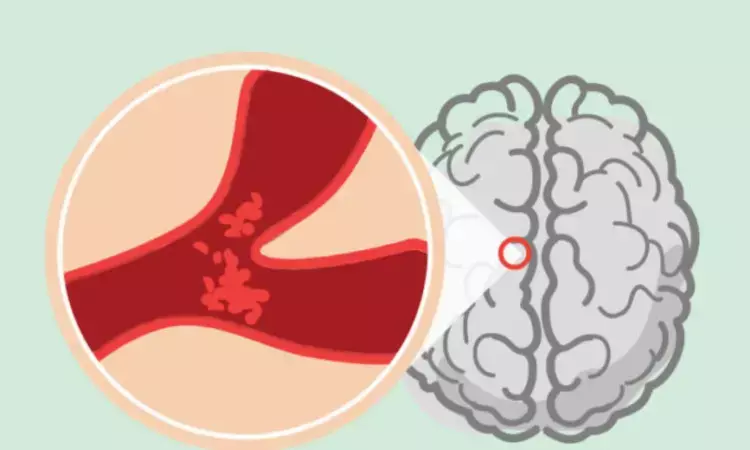
Melinda Roaldsen and peers found that intravenous tenecteplase given within 4·5 hours of awakening does not improves any functional outcome in patients with ischemic wake-up stroke selected using non-contrast CT. The findings were published in Lancet neurology.
This study was a multicenter, open-label, randomized controlled trial with blinded endpoint assessment, conducted at 77 hospitals in ten countries and it included patients aged 18 years or older with acute ischemic stroke symptoms upon awakening, limb weakness, a National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score of 3 or higher or aphasia, a non-contrast CT examination of the head, and the ability to receive tenecteplase within 4·5 hours of awakening.
Patients were randomly assigned to either a single intravenous bolus of tenecteplase 0·25 mg per kg of bodyweight (maximum 25 mg) or control (no thrombolysis) using a central, web-based, computer-generated randomization schedule. Trained research personnel, who conducted telephone interviews at 90 days (follow-up), were masked to treatment allocation.
The study found that treatment with tenecteplase was not associated with better functional outcome, according to modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score at 90 days. Mortality at 90 days did not significantly differ between treatment groups. Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage occurred in 6 (2%) patients in the tenecteplase group versus 3 (1%) in the control group. Any intracranial hemorrhage occurred in 33 (11%) versus 30 (10%) patients.
In conclusion, the study found that in patients with wake-up stroke selected with non-contrast CT, treatment with tenecteplase was not associated with better functional outcome at 90 days and the number of symptomatic hemorrhages and any intracranial hemorrhages in both treatment groups was similar to findings from previous trials of wake-up stroke patients selected using advanced imaging. Therefore, current evidence does not support treatment with tenecteplase in patients selected with non-contrast CT.
Source:
Roaldsen, M. B., Eltoft, A., Wilsgaard, T., Christensen, H., Engelter, S. T., Indredavik, B., Jatužis, D., Karelis, G., Kõrv, J., Lundström, E., Petersson, J., Putaala, J., Søyland, M.-H., Tveiten, A., Wu, T. Y., … Blair, C. (2022). Safety and efficacy of tenecteplase in patients with wake-up stroke assessed by non-contrast CT (TWIST): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. In The Lancet Neurology. Elsevier BV. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(22)00484-7
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


