- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
WHO recommends use of uterine balloon tamponade for treating postpartum hemorrhage
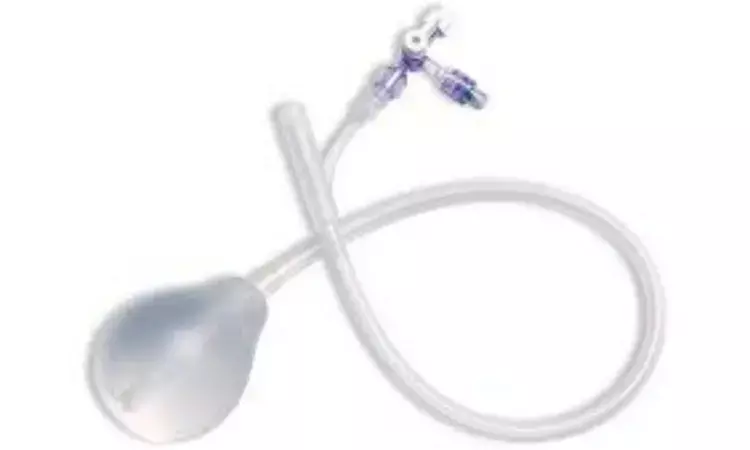
Delhi: A recent study in the journal Obstetrics & Gynecology reports the World Health Organization's (WHO) new recommendation on the use of the uterine balloon tamponade for the treatment of postpartum hemorrhage.
The recommendation that uterine balloon tamponade should be used only where there is already access to other postpartum hemorrhage treatments (including immediate recourse to surgery) has proved controversial. Especially, it is problematic for those working in low-level health care facilities in under-resourced settings, where there are already programs that have introduced low-cost uterine balloon tamponade devices for use, even in settings where recourse to surgical interventions is not possible. However, now, there are two separate randomized trials that both unexpectedly show unfavorable outcomes in these settings when a condom catheter uterine balloon tamponade device was introduced.
The WHO Guideline Development Group has developed a context-specific recommendation, stating that:
Uterine balloon tamponade is recommended for the treatment of postpartum hemorrhage due to uterine atony after vaginal birth in women who do not respond to standard first-line treatment, provided the following conditions are met:
- Immediate recourse to surgical intervention and access to blood products is possible if needed.
- A primary postpartum hemorrhage first-line treatment protocol (including the use of uterotonics, tranexamic acid, intravenous fluids) is available and routinely implemented.
- Other causes of postpartum hemorrhage (retained placental tissue, trauma) can be reasonably excluded.
- The procedure is performed by health personnel who are trained and skilled in the management of postpartum hemorrhage, including the use of uterine balloon tamponade.
- The maternal condition can be regularly and adequately monitored for prompt identification of any signs of deterioration.
To conclude, the WHO recommends that balloon tamponade should be used only where other supportive interventions are available if needed.
Reference:
Weeks, Andrew D. MD, FRCOG; Akinola, Oluwarotimi Ireti MD, FWACS; Amorim, Melania MD, PhD; Carvalho, Brendan MBBCh, FRCA; Deneux-Tharaux, Catherine MD, PhD; Liabsuetrakul, Tippawan MD, PhD; Meremikwu, Martin MBBCh, MSc; Miller, Suellen PhD, CNM; Nabhan, Ashraf MBBCh, MD; Nagai, Mari MD, PhD; Wahabi, Hayfaa FRCOG, PhD; Walker, Dilys MD World Health Organization Recommendation for Using Uterine Balloon Tamponade to Treat Postpartum Hemorrhage, Obstetrics & Gynecology: March 2022 - Volume 139 - Issue 3 - p 458-462 doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000004674
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


