- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Consumption of Diets rich in meat, oil, sugar, salt, and coffee linked to dysmenorrhea
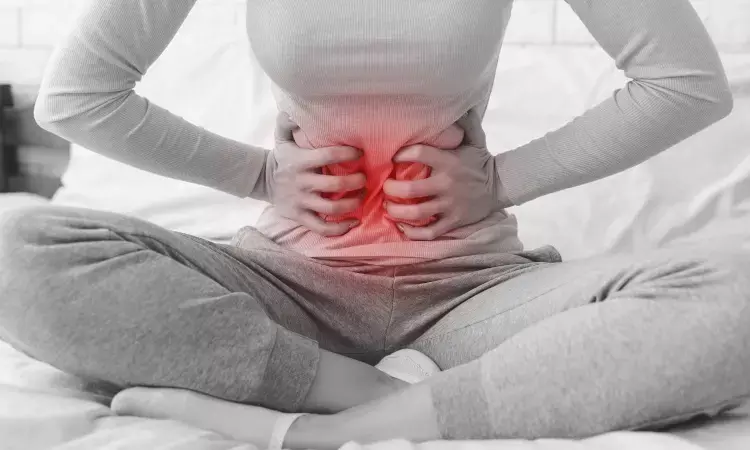
Dysmenorrhea is the leading cause of school absences for adolescent girls, but very few girls seek treatment for the same.
Researchers have conducted analysis of relevant studies and found that diet may be a key contributor, specifically diets high in meat, oil, sugar, salt, and coffee, which have been shown to cause inflammation.
Results of the research will be presented during The North American Menopause Society (NAMS) Annual Meeting in Atlanta, October 12-15, 2022.
Roughly 90% of adolescent girls experience menstrual pain. Most use over-the-counter medicine to manage the pain but with limited positive results. Evidence has highlighted that diets high in omega-3 fatty acids and low in processed foods, oil, and sugar reduce inflammation, a key contributor to menstrual pain.
This analysis was designed to study the effect of diet on menstrual pain and identify which foods contribute to it and which can reduce it. Research was conducted through a literature review that found multiple studies that examined dietary patterns that resulted in menstrual pain. In general terms, these studies found that diets high in omega-6 fatty acids promote inflammation and foods high in omega-3 fatty acids reduce it. The muscles in the uterus contract because of prostaglandins, which are active in inflammatory responses. When measuring the Dietary Inflammatory Index, it was found that those on a vegan diet (that excluded animal fat) had the lowest rates of inflammation.
"Researching the effects of diet on menstrual pain started as a search to remedy the pain I personally experienced; I wanted to understand the science behind the association. Learning about different foods that increase and decrease inflammation, which subsequently increase or reduce menstrual pain, revealed that diet is one of the many contributors to health outcomes that is often overlooked. I am hopeful that this research can help those who menstruate reduce the pain they experience and shed light on the importance of holistic treatment options," says Serah Sannoh, lead author of the poster presentation from Rutgers University.
"Since menstrual pain is a leading cause of school absenteeism for adolescent girls, it's important to explore options that can minimize the pain. Something like diet modification could be a relatively simple solution that could provide substantial relief for them," said Dr. Stephanie Faubion, NAMS medical director.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


