- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
MRI accurate and effective technique for identifying causes of abnormal uterine bleeding
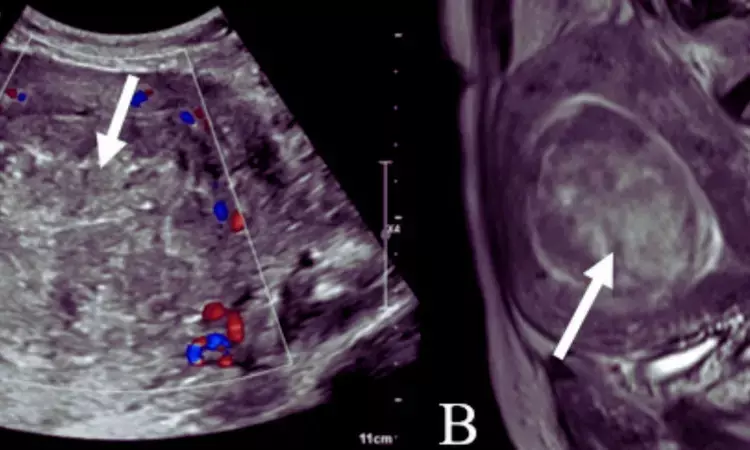
India: A recent study published in Cureus compared the effectiveness of ultrasonography (USG) and MRI for detecting the cause of abnormal uterine bleeding with pathological correlation.
The researchers found MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) to be the most effective method for accurately identifying the number, location, and characterization of extensions, lesions and staging of carcinomas.
The researchers reported, "The sensitivity of ultrasonography in polyps diagnosis was 66.66% since one case was misdiagnosed as submucosal fibroid, whereas the MRI sensitivity in polyps diagnosis was 100%. The sensitivity of USG in diagnosing adenomyosis was 77.78%, and MRI's in diagnosing adenomyosis was 100%."
In the study, the sensitivity of MRI and USG in fibroids detection was the same, i.e. 100%; however, MRI a was better for determining the exact location and number of lesions. USG and MRI sensitivity for malignancies detection was the same, i.e. 100%; however, MRI was better in evaluating the exact staging and depth of parametrial/myometrial involvement.
In gynecologic practice, abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) is one of the most common problems. It accounts for over 70% of all gynaecological complaints in the peri- and postmenopausal age group. Kalathuru Uhasai, Sri Devaraj Urs Academy of Higher Education and Research, Kolar, IND, and colleagues conducted an observational study comprising people with abnormal uterine bleeding.
Patients who presented with abnormal uterine bleeding were referred to the radiodiagnosis department and underwent ultrasonography of the pelvis and abdomen, followed by an MRI of the pelvis. Findings were analyzed and compared with the histopathological examination (HPE) of the samples of hysterectomized uterus, myomectomy, polypectomy, and dilation and curettage (D&C) of the endometrium.
The study revealed the following findings:
· Among the study population, ultrasonography reports SG showed 4.10% patients with polyps, 14.58% with adenomyosis, 52.08% with leiomyomas, and 29.16% with malignancies.
· On MRI examination, 6.25% of patients were diagnosed with polyps, 18.7% with adenomyosis, 45.8% with leiomyomas, and 29.16% were reported to have malignancies.
· The measure of agreement with the kappa value for MRI and HPE in evaluating the causes of abnormal uterine bleeding is 1.0 (very good).
· The kappa agreement value of USG and HPE in evaluating the causes of abnormal uterine bleeding is 0.903 (acceptable).
· The sensitivity of USG in diagnosing polyps, adenomyosis, leiomyoma, and malignancy was observed at 66%, 77.78%, 100%, and 100%, respectively.
· The sensitivity of MRI in diagnosing polyps, adenomyosis, leiomyoma, and malignancy was 100% for each.
"MRI is a non-invasive, accurate, and well-tolerated technique for identifying the causes of abnormal uterine bleeding, compared to ultrasonography, with great histological correlation," the researchers conclude. "It is an excellent and accurate preoperative imaging modality for locating, identifying, and determining the size of lesions."
Reference:
Uhasai, K., Naik, D., & P, R. (2023). Efficacy of MRI Over Ultrasound in Evaluation of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding With Histopathological Correlation. Cureus, 15(5). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.38560
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


