- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Optic nerve sheath diameter not linked with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, reveals research
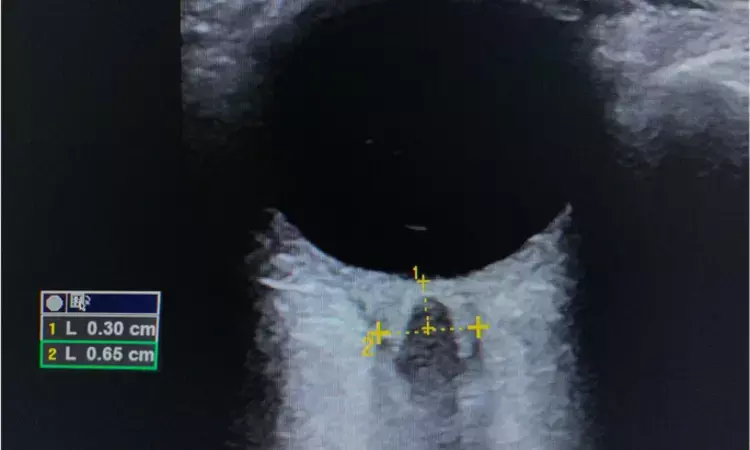
Optic nerve sheath diameter not linked with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, reveals research published in the BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.
Preeclampsia is implicated in 14% of maternal deaths worldwide, mostly due to complications such as intracranial hemorrhage and cerebral edema. Cerebral edema increases intracranial pressure, which can be predicted by ultrasonographic measurement of the optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD). Greater diameters have been reported in women with preeclampsia and eclampsia; however, data are lacking on the possible association with maternal and neonatal adverse outcomes.
This study aimed to determine whether there is an association between hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and the ONSD, and between this measurement and maternal and neonatal adverse outcomes. This was a cohort study involving 183 women in the third trimester of pregnancy or within 24 h following childbirth, distributed as follows: control group (n = 30), gestational hypertension (n = 14), chronic hypertension (n = 12), preeclampsia without severe features (n = 12), preeclampsia with severe features (n = 62), superimposed preeclampsia (n = 23) and eclampsia (n = 30).
The participants underwent ocular ultrasonography, and data on maternal and neonatal outcomes were collected from the medical records. To compare the groups, analysis of variance was used for the normally distributed numerical variables and the Kruskal–Wallis test was used for variables with non-normal distribution. Two-tailed p-values ≤ 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Results: Overall comparison between the seven groups showed no statistically significant difference in the mean ONSD (p = 0.056). Nevertheless, diameters were significantly greater in the eclampsia group compared to the control group (p = 0.003). Greater diameters were associated with maternal admission to the intensive care unit (ICU) (p < 0.01) and maternal near miss (p = 0.01).
There was no association between ONSD and admission to the neonatal ICU (p = 0.1), neonatal near miss (p = 0.34) or neonatal death (p = 0.26). No association was found between ONSD and the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy in the overall analysis; however, ONSD was greater in women with eclampsia compared to controls. Greater diameters were associated with maternal admission to the ICU and maternal near miss. These findings suggest a potential use for bedside ultrasound as an additional tool for stratifying risk in patients with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy.
Reference:
da Mota, M.F., de Amorim, M.M., Correia, M.D.T. et al. The optic nerve sheath in hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and perinatal outcomes: a cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 24, 654 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-024-06858-5
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


