- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Additional imaging techniques detect early stage cancers missed by mammograms in women with dense breasts: The Lancet
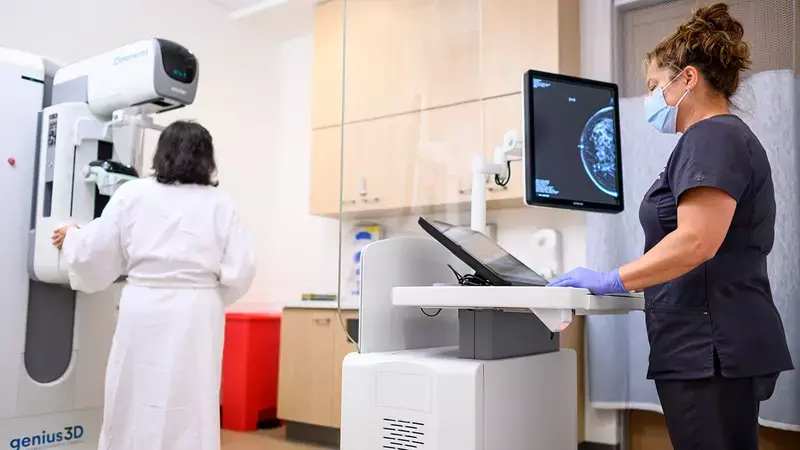
In women with dense breasts (breasts with relatively low levels of fatty tissue) and a negative mammogram, supplemental imaging techniques detect early-stage cancers, with imaging techniques three times more effective than ultrasound, finds a phase 3 randomised control trial published in The Lancet.
Women with extremely dense breasts, about 10% of those aged 50-70 years in the UK, face a fourfold increased risk of breast cancer compared to those with the least dense breasts*. Mammograms are less effective for detecting early-stage cancer in dense breasts, as the tissue can hide tumours on the breast x-rays. Previous studies have shown MRI and ultrasound are effective supplementary imaging methods, but this study is the first to compare them with contrast mammography in women with normal mammograms and dense breast tissue.
Over 9000 women in the UK with dense breasts and a negative mammogram were randomly allocated to one of three different supplementary techniques. The cancer detection rate for the imaging techniques was 1.7% (for a fast MRI) and 1.9% (for contrast mammography), whilst the cancer detection rate for the ultrasound group was 0.4%.
Authors highlight that although this study shows the scans can detect additional small cancers which are likely to save lives, further research is needed to confirm whether they could reduce the number of deaths due to breast cancer, to establish the risk of overdiagnosis and to estimate the cost benefit ratio of implementing a supplemental imaging strategy for breast cancer screening.
Lead author, Professor Fiona Gilbert, University of Cambridge (UK) says, “In addition to the relevance for the UK’s breast cancer screening programme, this study has global implications for all countries where screening is undertaken for women with dense breast tissue.”
Reference:
Gilbert, Fiona J et al., Comparison of supplemental breast cancer imaging techniques-interim results from the BRAID randomised controlled trial, The Lancet, DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(25)00582-3.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


