- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Personalized, 3D printed shields may protect patients during radiation therapy
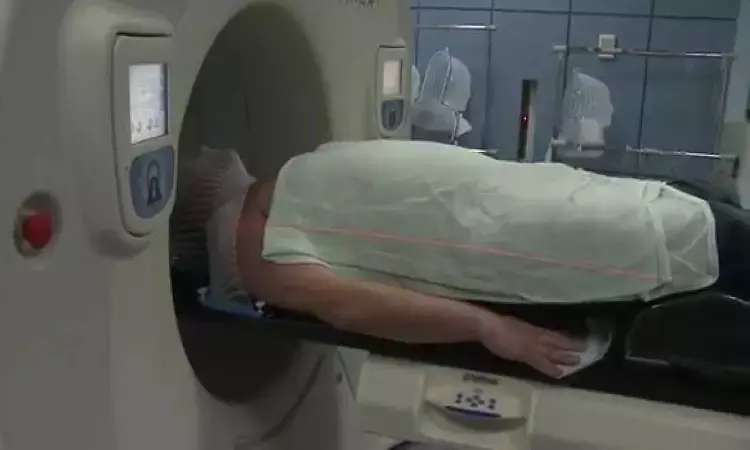
BOSTON -- Radiation therapy is used as a treatment for more than half of all cancer patients and can be highly effective at shrinking tumors and killing cancer cells. But radiation treatment can also damage healthy tissue, including tissue in the mouth and gastrointestinal tract. This tissue injury can lead to oral mucositis, esophagitis, and proctitis -- painful and sometimes debilitating tissue damage. It's estimated that these injuries occur in over 200,000 patients in the U.S. each year. In a new paper published in Advanced Science, investigators from Brigham and Women's Hospital, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital and MIT describe efforts to develop a new personalized, 3D-printed device intended to shield patients who are undergoing radiation therapy and prevent radiation-induced toxicity. The work to date has been conducted in preclinical models and uses simulations to predict effects in humans, laying groundwork for clinical trials for patients.
"When we treat patients with radiation, we do our best to minimize the area of healthy tissue that receives radiation and break up treatment into small doses, but it's a fine balance. We want to administer the most dose we can to shrink the tumor without causing damage to healthy tissue," said lead author James Byrne, MD, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher in the Traverso lab at the Brigham and MIT and a senior resident physician in Radiation Oncology at Brigham, MGH, and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. "Our goal through this project was to find an innovative solution that could offer personalized protection for patients."
Byrne collaborated with a multi-disciplinary team on the work, including experts in radiation oncology, physicists, mechanical engineers, and gastroenterologists.
"It's not uncommon for gastroenterologists to be called in to consult on a case to support a patient who is experiencing side effects of radiation in the esophagus, small intestine or anywhere else in the gastrointestinal tract," said corresponding author C. Giovanni Traverso, MB, BChir, PhD, a gastroenterologist and biomedical engineer in the Division of Gastroenterology at the Brigham and MIT. "A couple of years ago, James and I began brainstorming -- what if we could develop a shield that could help protect a significant portion of normal tissue in the radiation field?"
Byrne and colleagues tested a broad range of materials -- both solid and liquid -- from which to construct the radioprotective shields. The team focused on high atomic number (Z) materials, which can prevent gamma and X-rays from passing through, and other materials to reduce radiation backscatter. Using CT scans from patients, the team created designs unique to individual patients and used 3D-printing to generate them. They tested their shields in rats and pigs. They found that the shields could protect healthy tissue in the mouth and rectum in rats with good feasibility and reproducibility of placement in pigs. In simulations of human patients, the team estimated that the device could reduce radiation to areas in the mouth by 30 percent for head and neck cancer patients, and in the gastrointestinal tract by 15 percent in prostate cancer patients, without reducing radiation dose to the tumor.
The authors note that this work is an initial proof-of-concept study and additional investigations will be needed to translate the devices for use in the clinic. However, their results so far suggest that personalized shields could someday help reduce the risk of radiation toxicity.
"Our results support the feasibility of personalized devices for reducing the side effects of radiation therapy," said Byrne. "This personalized approach could be applicable to a variety of cancers and holds the potential to reduce the burden of radiation injury and toxicity for our patients."
http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/advs.202100510
Hina Zahid Joined Medical Dialogue in 2017 with a passion to work as a Reporter. She coordinates with various national and international journals and association and covers all the stories related to Medical guidelines, Medical Journals, rare medical surgeries as well as all the updates in the medical field. Email: editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


