- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Proton Pump Inhibitors Linked to Worse Survival in Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma: Study
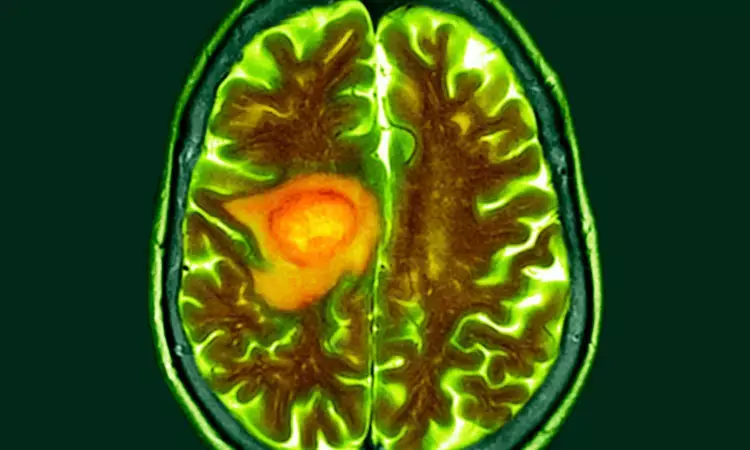
A new study published in the Journal of American Medical Association showed that in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma, proton pump inhibitors (including ALDH1A1-activating PA-PPIs), which are frequently used to avoid steroid-related gastritis, were linked to worse survival outcomes.
The patients with glioblastoma are frequently taken proton pump inhibitors (PPI) to avoid steroid-induced gastritis and peptic ulcer disease. However, these medications may increase the activity of aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 A1 (ALDH1A1), which has been connected to defense against chemotherapy, radiation, and oxidative stress. Thus, this study investigated the relationships between outcomes in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma and the use of powerful ALDH1A1-activating PPIs (PA-PPIs) and other antacid medications.
This meta-analysis used a dataset of 5 randomized clinical trials carried out between 2008 and 2020 to do a secondary analysis of individual prospectively collected patient data. Patients who had just been diagnosed with glioblastoma were among the participants. In November 2024, the data analysis was finished.
This study determined three landmarks; the beginning of temozolomide maintenance cycles 1 (landmark 1) and 4 (landmark 2), as well as the conclusion of cycle 6 (landmark 3). They also evaluated medication usage at baseline. Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) from baseline and the beginning of each matching landmark period were the main outcome measures.
There were 2981 patients in the study population. The patients receiving PA-PPI showed lower PFS and OS at all four time periods according to univariate analysis. PFS at landmarks 1 (hazard ratio [HR], 1.14 [95% CI, 1.01-1.28]), 2 (HR, 1.26 [95% CI, 1.09-1.44]), and 3 (HR, 1.31 [95% CI, 1.10-1.56]), and OS at landmarks 1 (HR, 1.34 [95% CI, 1.08-1.66]) and 2 (HR, 1.14 [95% CI, 1.01-1.29]).
The usage of other antacid medications did not show any such correlation. Independent of MGMT promoter methylation and steroid usage, PA-PPI use was found to be negatively correlated with PFS and OS.
Overall, PPI usage was linked to worse outcomes in this meta-analysis of patients with recently diagnosed GBM. These results imply that routine preventive PPI usage should be avoided in glioblastoma patients since there are other treatments available, like H2 blockers or locally acting antacids, and because a negative impact cannot be ruled out.
Source:
Le Rhun, E., Sain, D., Erridge, S. C., Reardon, D. A., Minniti, G., Roth, P., Wick, W., Nabors, B., Sampson, J., Mason, W., Cloughesy, T., Reijneveld, J. C., Stupp, R., Preusser, M., Gorlia, T., & Weller, M. (2025). Proton pump inhibitor use and survival in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. JAMA Network Open, 8(11), e2545578. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.45578
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


