- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Totally implanted ports preferable in patients receiving SACT for solid tumours: Lancet
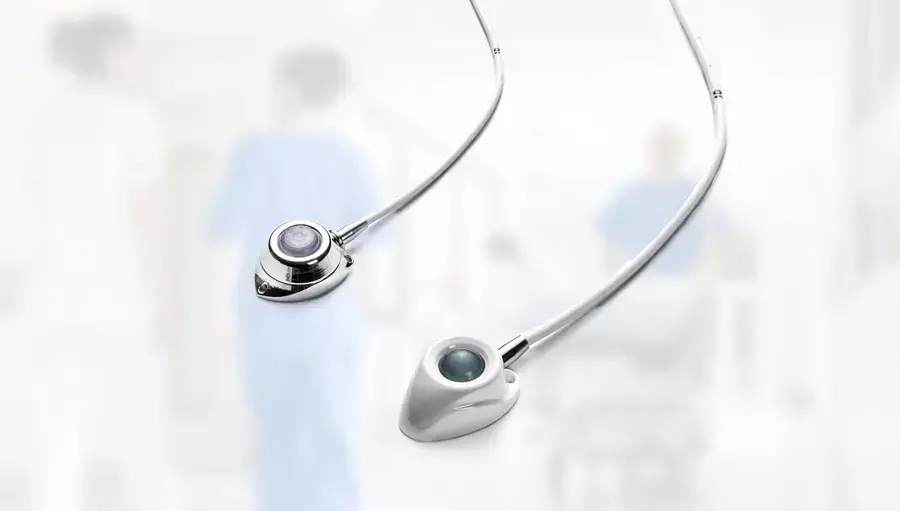
Totally implanted ports (PORTs) are comparatively superior to Hickman and PICCs in terms of efficacy and safety in patients receiving systemic anticancer treatment (SACT) for treating solid tumours, suggests a study published in the Lancet.
Hickman-type tunnelled catheters (Hickman), peripherally inserted central catheters (PICCs), and totally implanted ports (PORTs) are generally used to deliver systemic anticancer treatment (SACT) via a central vein.
A group of researchers from the United Kingdom conducted a study to compare complication rates and costs of the three devices to establish acceptability, clinical effectiveness, and cost-effectiveness of the devices for patients receiving SACT.
The researchers performed an open-label, multicentre, randomised controlled trial (Cancer and Venous Access [CAVA]) of three central venous access devices: PICCs versus Hickman (non-inferiority; 10% margin); PORTs versus Hickman (superiority; 15% margin); and PORTs versus PICCs (superiority; 15% margin).
Adults receiving SACT for more than or equal to 12 weeks for solid or haematological malignancy from 18 oncology units in the UK were included. Between Nov 8, 2013, and Feb 28, 2018, of 2714 individuals screened for eligibility, 1061 were enrolled and randomly assigned, contributing to the relevant comparison or comparisons. Four randomisation options were available:
- Hickman versus PICCs versus PORTs (2:2:1)
- PICCs versus Hickman (1:1)
- PORTs versus Hickman (1:1)
- PORTs versus PICCs (1:1)
Randomisation was done using a minimisation algorithm stratifying by centre, body-mass index, type of cancer, device history, and treatment mode.
The primary outcome was complication rate assessed until device removal, withdrawal from the study, or 1-year follow-up.
The results of the study are as follows:
- Similar complication rates were observed for PICCs (110 [52%] of 212) and Hickman (103 [49%] of 212).
- Although the observed difference was less than 10%, non-inferiority of PICCs was not confirmed potentially due to inadequate power.
- PORTs were superior to Hickman with a complication rate of 29% versus 43%
- PORTs were superior to PICCs with a complication rate of 32% versus 47%
The researchers concluded that for most patients receiving SACT, PORTs are more effective and safer than both Hickman and PICCs. Our findings suggest that most patients receiving SACT for solid tumours should receive a PORT within the UK National Health Service.
Reference:
Central venous access devices for the delivery of systemic anticancer therapy (CAVA): a randomised controlled trial by Moss J et. al published in the Lancet.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00766-2
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


