- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
AI Accurately Detects BPD and Pulmonary Hypertension From Retinal Images in Preterm Infants: Study
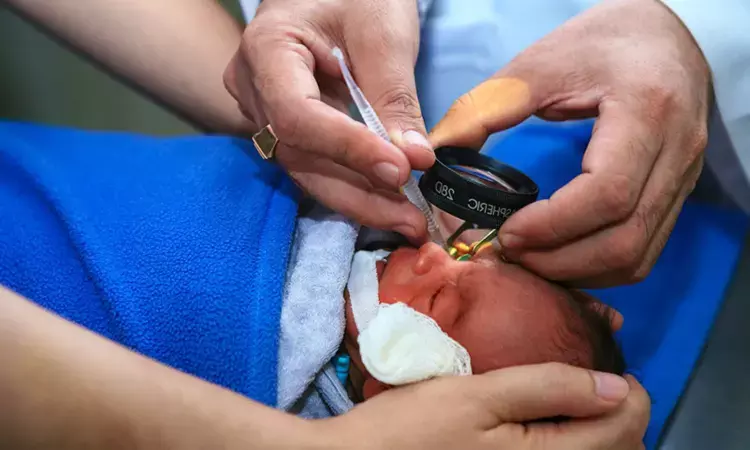
A new study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association showed that using retinal scans of premature infants, artificial intelligence may be able to accurately diagnose pulmonary hypertension (PH) and bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD).
A novel, non-invasive method for predicting cardiac illness in premature infants is provided via deep learning analysis of retinal pictures. These models have the potential to advance precision medicine in neonatal care by enabling early risk classification, better monitoring, and prompt therapies through the identification of subtle vascular and anatomical patterns. Therefore, this study evaluated whether features linked to BPD or PH in infants could be found in images acquired as part of retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) screening.
Retinal pictures from patients participating in the multi-institutional Imaging and Informatics in Retinopathy of Prematurity (i-ROP) project were analyzed using a deep learning model. From 2012 to 2020, infants at risk for ROP who underwent routine ROP screening exams were included in the analysis. Seven neonatal intensive care units provided the infants. In order to avoid the clinical diagnosis of BPD or PH, images were restricted to 34 weeks or less postmenstrual age (PMA).
This analysis included 493 newborns (mean [SD] gestational age, BPD, 25.7 [1.8] weeks; normal, 27.3 [1.8] weeks; 267 male [54.2%]). A held-out test set of 37 patients from the PH cohort and 99 patients from the BPD cohort was used to report performance. The accuracy of the multimodal model for BPD was higher than that of the demographics-only (0.72; ∆AUC, 0.1; 95% CI, −0.008 to 0.21; P =.07) or imaging-only (0.72; ∆AUC, 0.1; 95% CI, 0.04-0.16; P =.002) models.
The multimodal AUC for PH was 0.91 compared to the demographics-only 0.68 (∆AUC, 0.14; 95% CI, 0.006-0.27; P =.04) and imaging-only 0.91 (∆AUC, −0.09; 95% CI, −0.3 to 0.12; P =.40) models. When trained on photos without clinical ROP symptoms, the results remained consistent. Overall, in preterm newborns, retinal pictures acquired during ROP screening may be utilized to predict the diagnosis of BPD and PH.
Source:
Singh, P., Kumar, S., Tyagi, R., Young, B. K., Jordan, B. K., Scottoline, B., Evers, P. D., Ostmo, S., Coyner, A. S., Lin, W.-C., Gupta, A., Erdogmus, D., Chan, R. V. P., McCourt, E. A., Barry, J. S., McEvoy, C. T., Chiang, M. F., Campbell, J. P., & Kalpathy-Cramer, J. (2026). Deep learning-based prediction of cardiopulmonary disease in retinal images of premature infants. JAMA Ophthalmology. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2025.5814
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


