- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Compounded Imiquimod has Potential Role in Treatment of Ocular Surface Malignancies: JAMA
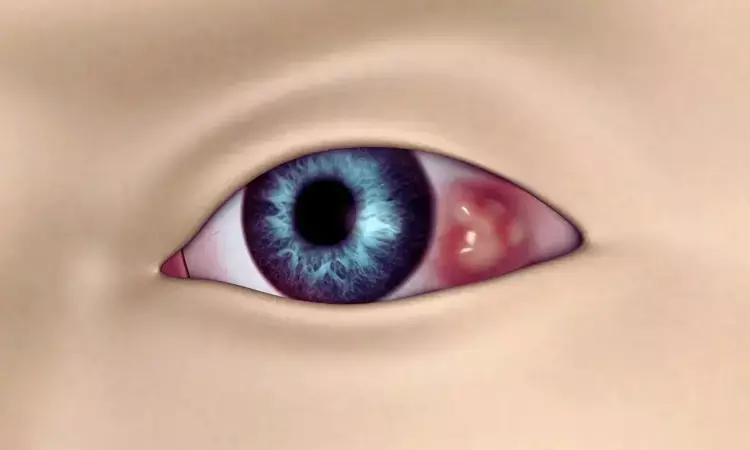
USA: Researchers have found in a small case series that a compounded form of imiquimod, a topical immune-response modifier, showed promising effectiveness in treating ocular surface malignancies. The therapy appeared relatively safe, though the sample size was limited. Currently, these malignancies are typically managed surgically or with off-label topical agents like 5-fluorouracil or mitomycin C, which can be toxic to the ocular surface.
- Three of the five patients achieved complete clinical and histological resolution after 12 weeks of imiquimod therapy.
- Two patients showed partial responses, indicating meaningful but incomplete improvement.
- Complete clearance was observed in cases of conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) with moderate dysplasia.
- One squamous cell carcinoma case showed partial downgrading to CIN with moderate dysplasia.
- No histological recurrence was seen at previously positive surgical margins.
- Patients with conjunctival melanoma in situ (MIS) had partial clinical improvement, while biopsy-confirmed areas demonstrated full histologic resolution.
- A patient with primary acquired melanosis (PAM) showed complete clinical and histological clearance after 15 weeks of treatment.
- No serious adverse events occurred during treatment.
- All five patients experienced mild to moderate ocular surface or eyelid irritation.
- These adverse effects resolved within one to two weeks after taking a drug holiday or completing therapy, indicating good overall tolerability.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


