- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Early intervention for idiopathic full thickness macular holes provide better visual outcomes: Study
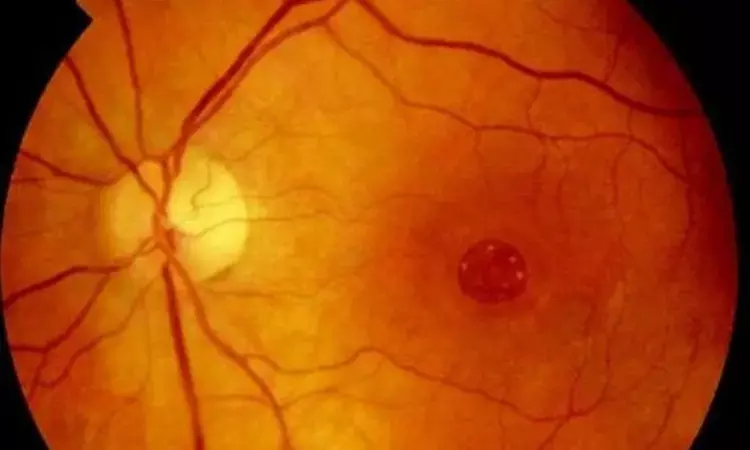
In a new study conducted by Declan C. Murphy and team, it was shown that in patients undergoing surgery for idiopathic full thickness macular holes (iFTMH), symptom duration was independently correlated with both structural and visual results. The findings of this study were published in Ophthalmology Journal.
IFTMH has an incidence of up to 0.5% and are visually incapacitating. Best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) drops to 20/200 when left untreated. Surgery can restore eyesight and repair holes. Although the impact of symptom duration on surgical results is unknown. Therefore, using individual participant data (IPD) research of randomized controlled trials, this study sought to establish the impact of symptom duration on outcomes in patients having surgery for iFTMH. Primary iFTMH completion and post-operative best corrected visual acuity were the outcomes evaluated.
For this study, in people with iFTMH who had vitrectomy with gas tamponade, a systematic review found eligible RCTs in which symptom duration, primary iFTMH closure, and post-operative BCVA were noted. The search for publications published between 2000 and 2020 was conducted using bibliographic databases.
The key findings of this review were:
1. There were 20 qualifying RCTs found. Data from all research was sought, and 12 studies, totaling 940 eyes, provided the data.
2. The median number of months with symptoms was 6.
3. In 81.5% of eyes, primary closure was accomplished.
4. Predicted likelihood of closure and symptom duration had a linear relationship.
5. According to multilevel logistic modeling, the probabilities of closure were 0.965 times lower for every extra month of duration.
6. Primary closure was more likely in patients who had internal limiting membrane (ILM) peeling, intra-operative ILM flap usage, improved pre-operative BCVA, face-down orientation, and lower iFTMH sizes.
7. In eyes that experienced primary closure, the average post-operative BCVA was 0.52 logMAR (20/66).
8. For eyes that had already experienced primary iFTMH closure, multilevel logistic regression revealed that each extra month of symptom persistence was linked to a 0.008 logMAR unit deterioration in BCVA.
9. Improved post-operative BCVA was also linked to ILM flaps, intra-ocular tamponade with long-acting gas, better pre-operative BCVA, lower iFTMH size, and phakic status.
In conclusion, the authors recommend that patients with primary macular holes, especially those with smaller macular holes, be sent for surgery at the earliest to preserve eyesight.
Reference:
Murphy, D. C., Al-Zubaidy, M., Lois, N., Scott, N., & Steel, D. H. (2022). The effect of macular hole duration on surgical outcomes: An individual participant data study of randomised controlled trials. In Ophthalmology. Elsevier BV. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2022.08.028
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


