- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Higher cumulative anti-VEGF injections may worsen cognitive health: Study
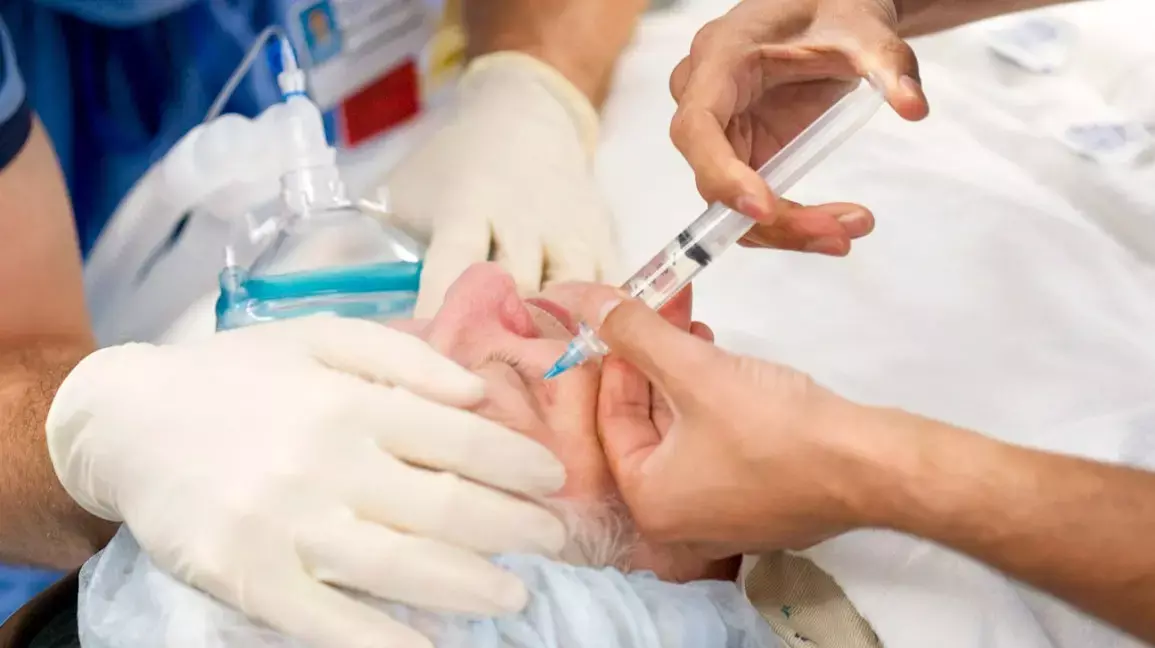
Cognitive health worsens with higher cumulative anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Injections injections in Macular Degeneration patients, suggests a study published in the Retina Journal.
After intravitreal injection, anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) agents are found in the systemic circulation and can suppress systemic VEGF levels. Neuronal health and cognitive function in the central nervous system have been associated with normal physiological levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression.
A team of researchers from the U.S.A conducted a study to determine whether there was an association between cumulative anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) exposure and cognitive function.
One hundred and seventy-five patients aged sixty-five to eighty-five with the vision of at least 20/50 or better in one eye and a diagnosis of age-related macular degeneration took an iPad-based brain health assessment to determine their risk of mild cognitive impairment. The result for each patient was compared with the total number of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) injections per individual patient. Patients were then stratified into groups with 0 injections (control), 1 to 9 injections, ten to twenty injections, or greater than 20 injections.
The results of the study are as follows:
- The group of patients with more than twenty injections had a higher likelihood of mild cognitive impairment compared with the control group, with statistically significant worse mean Z-scores.
Thus, the researchers concluded that worsening cognitive health with higher cumulative anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) injections. This study was not designed to show a causal link but does suggest that additional investigation is required to demonstrate a causal link between intravitreal therapy and cognitive changes.
Reference:
A study titled, "Brain Health Assessment In Macular Degeneration Patients Undergoing Intravitreal Anti–Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Injections (The Bham Study): An Interim Analysis" by Ray, Subhransu K. and Manz, Sarah N. published in the Retina Journal.
DOI: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000003066
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


