- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
COVID-19 infection linked to Increased Retinal Vascular Occlusions: JAMA
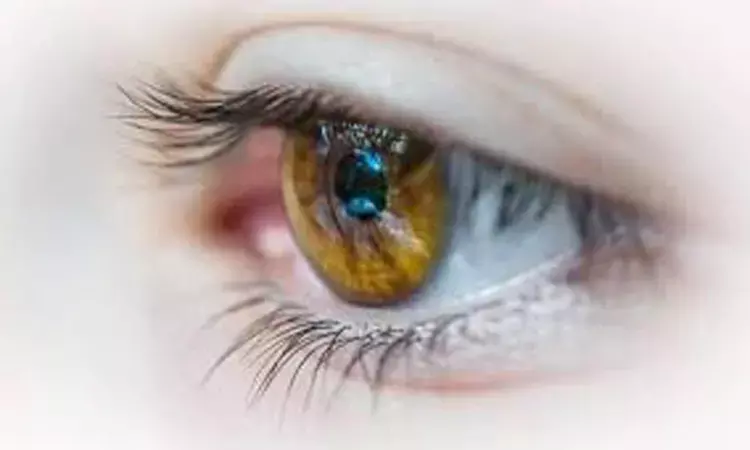
New findings published in the Journal of American Medical Association affirm that there was an increasing incidence of retinal vein occlusions (RVOs) following COVID-19 infection; however, these occurrences are still rare, and a cause-and-effect link cannot be proved in the absence of randomized controlled trials.
COVID-19 has been linked to systemic vascular injury; however, the danger to the retinal vasculature is yet unknown. As a result, Bobeck S. Modjtahedi and colleagues undertook this investigation to see if the prevalence of retinal vascular occlusions changed following COVID-19 infection.
Participants without a background of retinal vascular occlusion who were confirmed with COVID-19 infection between January 20, 2020, and May 31, 2021 were enrolled in this cohort research at an integrated health care organization (Kaiser Permanente Southern California). Participants were excluded if they had a background of retinal artery occlusions (RAOs) or retinal vein occlusions (RVOs) more than 6 months before to their COVID-19 diagnosis, or if they had been enrolled in Kaiser Permanente Southern California for less than 6 months prior to their COVID-19 diagnosis. all the participants with COVID-19 were included for this study. The primary finding of this study was a decrease in the average biweekly incidence of new RAOs and RVOs following a COVID-19 diagnosis.
The key findings of this study were as follow:
1. This study includes 432 515 individuals who have been diagnosed with COVID-19 infection.
2. The mean (SD) age was 40.9 (19.2) years, and 231 767 (53.6%) of the patients were female.
3. In the six months following COVID-19 diagnosis, sixteen individuals had a RAO and 65 had an RVO.
4. After controlling for age, gender, self-reported race and ethnicity, body mass index, history of diabetes, hypertension, or hyperlipidemia, and hospitalization, the incidence of new RVOs was greater 6 months after COVID-19 infection compared to 6 months before infection.
5. There was a modest rise in RAOs following a COVID-19 diagnosis.
6. RAOs and RVOs were most common 10 to 12 weeks and 6 to 8 weeks following COVID-19 diagnosis, respectively.
In conclusion, when evaluating patients following infection, clinicians must evaluate the probable link between COVID-19 infection and retinal vascular occlusions. The findings add to the evidence of COVID-19-induced prothrombosis and suggest that the effects of the infection may linger for several weeks. Large epidemiologic investigations are needed to further establish the link between COVID-19 infection and retinal thromboembolic events.
Reference:
Modjtahedi BS, Do D, Luong TQ, Shaw J. Changes in the Incidence of Retinal Vascular Occlusions After COVID-19 Diagnosis. JAMA Ophthalmol. Published online April 14, 2022. doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2022.0632
Medical Dialogues consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


