- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Lotilaner Ophthalmic Solution Promising Treatment for Demodex Blepharitis: Study
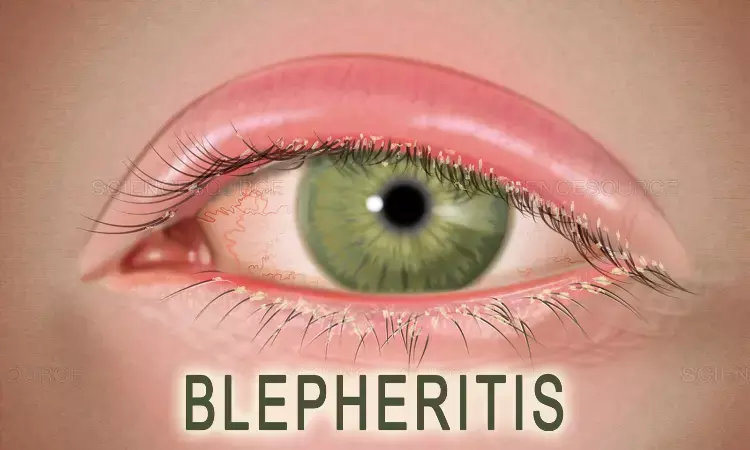
Demodex blepharitis, caused by an infestation of Demodex mites, poses a significant burden on affected individuals, impacting their quality of life. Traditional management options have been associated with adverse effects, prompting the search for novel therapeutic alternatives. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis assessed the safety and efficacy of lotilaner ophthalmic solution (0.25%) as a treatment for Demodex blepharitis. The study was published in the American Journal Of Ophthalmology. The study was conducted by Talha M. and colleagues.
Demodex blepharitis affects millions of individuals worldwide, leading to various ocular manifestations. Prior management strategies, including topical tea tree oil and antibiotics, were associated with adverse effects. Lotilaner, an antiparasitic compound, offers a targeted approach for Demodex eradication.
The systematic review included data from four randomized controlled trials and two single-arm studies, comprising a total of 328 neonates. Studies were selected based on eligibility criteria, including treatment with lotilaner ophthalmic solution and assessment of Demodex mite eradication and collarette score.
The key findings of the study were:
• Effectiveness of Lotilaner:
Lotilaner ophthalmic solution demonstrated efficacy in eradicating Demodex mites compared to the control group (RR, 3.55; 95% CI, 2.87 - 4.40; P < .00001).
The intervention cohort showed a significantly improved clinically meaningful collarette score compared to the control cohort (RR, 3.15; 95% CI, 2.56 - 3.89; P < .00001).
• Safety Profile:
Rare adverse effects, including mild burning, redness, and blurriness, were reported with lotilaner treatment, reaffirming its favourable safety profile.
Lotilaner ophthalmic solution (0.25%) emerges as a promising treatment option for Demodex blepharitis, offering efficacy in mite eradication and improvement in collarette scores. The findings underscore its potential as a specific and well-tolerated therapy, enhancing the management of this common ocular condition.
The approval of lotilaner by the FDA signifies a significant advancement in the management of Demodex blepharitis. Its targeted mechanism of action and favourable safety profile position it as a valuable addition to existing treatment strategies, benefiting patients and healthcare providers alike.
Reference:
Talha M, Haris Ali M, Fatima E, Nadeem A, Ahmed A, Nashwan AJ. Efficacy and Safety of Lotilaner Ophthalmic Solution (0.25%) for the Treatment of Demodex Blepharitis: A GRADE Assessed Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational & Experimental Studies. Am J Ophthalmol. Published online March 19, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2024.03.019
Dr Riya Dave has completed dentistry from Gujarat University in 2022. She is a dentist and accomplished medical and scientific writer known for her commitment to bridging the gap between clinical expertise and accessible healthcare information. She has been actively involved in writing blogs related to health and wellness.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


