- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Nepafenac punctal plug reduces Postop Pain After Cataract Surgery
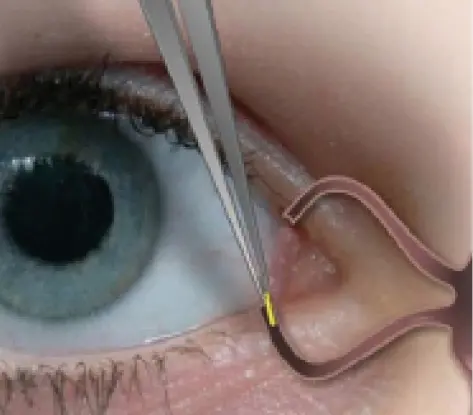
The topical approach of dispensing drug is the most common drug delivery system for pain management after cataract surgery. However, the topical ocular drug bioavailability is notoriously poor, in the order of 5% or less. A recent study suggests that the nepafenac punctal plug drug delivery system (PPDS) is safe and effective for reducing pain and inflammation associated with cataract surgery. The study findings were published in the Journal of Cataract and Refractory Surgery in the February 2021 issue.
The outcomes in contemporary cataract surgery partially depend on patient compliance. New therapeutic approaches, such as the one presented in this study, represent an appealing alternative. "The nepafenac PPDS simplifies medical management for the elderly patient population and resolves the problems associated with the use of topical medication. It demonstrated unprecedented efficacy in reducing pain and inflammation after cataract surgery in the phase II study." Dr Eric D. Donnenfeld said in an interview.
Dr Eric D. Donnenfeld and the team conducted a phase 2 study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a nepafenac punctal plug delivery system (N-PPDS) after cataract surgery.
It was a prospective, multicenter, randomized (2:1), parallel-arm, double-masked, placebo-controlled, phase II pilot study of 56 patients. Researchers randomly assigned them to receive either experimental N-PPDS (n=38) or placebo (n=18). All eyes underwent routine unilateral cataract surgery with intraocular lens implantation. The major outcomes assessed were postoperative ocular pain and inflammation.
Key findings of the study were:
• Upon evaluation, researchers found that the N-PPDS group had a significantly higher percentage of pain-free patients than that in the p-PPDS group (22/32 [69%] vs 6/16 [38%] at 3days; and 24/36 [67%] vs 5/16 [31%] at 7days).
• They also found that about 52% of patients in the N-PPDS cohort were pain-free at all postoperative visits compared with 0% in the placebo group.
• On day 7, they noted that the anterior chamber cell scores were better in the N-PPDS group.
• They also noted that the plug retention rate in the overall group was 98.2%, with plug extrusion occurring in one patient in the N-PPDS group who was excluded from the analysis.
The authors concluded, "The Evolute punctal plug delivery system for sustained drug delivery of nepafenac during cataract surgery is safe and effective in controlling postoperative pain and inflammation associated with surgery."
For further information:
Medical Dialogues Bureau consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


