- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
OCT angiography can detect microvascular changes predictive of normal-tension glaucoma
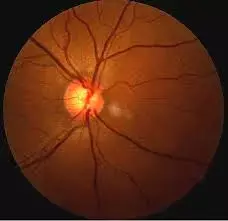
Optical coherence tomography angiography can detect microvascular changes predictive of normal-tension glaucoma suggests a recent study published in the American Journal of Ophthalmology
A study was conducted to investigate the contribution of vessel parameters to identify normal tension glaucoma (NTG) suspects at risk of normal tension glaucoma development. It was a multicenter prospective cohort study.
A total of 307 eyes of 307 normal tension glaucoma suspects having intraocular pressure within the normal range; a suspicious optic disc, but without definite localized retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) defects; and a normal visual field (VF).
To measure laminar vessel density (VD), the vessel density was measured in the intradiscal region from images of the deep vascular layers of optical coherence tomography angiography (OCT-A). Conversion to normal tension glaucoma was defined either by a new localized RNFL defect in the superotemporal or inferotemporal region, or the presence of a glaucomatous visual field defect on two consecutive tests according to the pattern standard deviation plots.
The Results of the study are:
- In total, 73 (23.8%) of the 307 normal tension glaucoma suspects converted to normal tension glaucoma during the follow-up period of 59.84 ± 12.44 months.
- The detection rate of microvasculature dropout (MvD) was significantly higher in normal tension glaucoma suspects who progressed to normal tension glaucoma (50.7%) than in those who did not
- The macular deep vessel density and laminar deep vessel density were significantly lower in normal tension glaucoma suspects who progressed to normal tension glaucoma.
- The presence of MvD and lower laminar deep vessel density were significantly associated with normal tension glaucoma conversion.
Thus, Normal tension glaucoma suspects with baseline MvD or a lower laminar deep vessel density on OCT-A had a higher risk of conversion.
Reference:
Younhea Jung et al. Microvasculature Dropout and Development of Normal Tension Glaucoma in Glaucoma Suspects: The Normal Tension Glaucoma Suspect Cohort Study. Published:August 03, 2022DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2022.07.020
Keywords:
Optical, coherence, tomography, angiography, detect, microvascular, changes, predictive, normal-tension, glaucoma, American Journal of Ophthalmology, Glaucoma, Glaucoma suspect, Microvasculature dropout, Optical, Coherence, Tomography Angiography, Younhea Jung, Hae-Young Lopilly Park, Heejong Shin, Si Eun Oh, Seong Ah Kim, Ji-Young Lee, Da Young Shin, Soo Ji Jeon, Yong-Chan Kim, Hye-Young Shin, Jin A Choi, Na Young Lee, Chan Kee Park
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


