- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Pentosan Polysulfate Use Linked to Increased Risk of Maculopathy, finds research
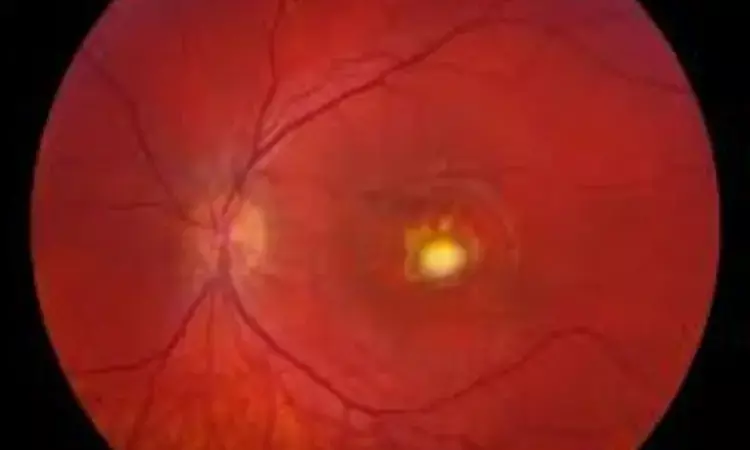
Researchers showed that antibiotic therapy with pentosan polysulfate (PPS) is associated with a significant risk of maculopathy, a leading cause of severe impairment of vision in any stage of the disease. The results derive from a nationwide, population-based Asian study of more than 300,000 individuals diagnosed with cystitis. The study was conducted by Kim and colleagues and was published in the journal of Ophthalmology.
This was a retrospective cohort study with 103,553 in the PPS user group and 205,792 in the non-user group, all who were newly diagnosed with cystitis between 2009 and 2020. This sample size was adequate to give a substantial basis for analyzing the potential risks associated with PPS. The two groups were followed over time to establish whether the incidence of maculopathy occurred following the use of PPS.
To establish the association between the use of PPS and maculopathy, researchers applied a time-dependent Cox proportional hazard model. Two sensitivity analyses were also conducted for those with a cumulative dose above 9 grams of PPS.
• The use of PPS was significantly associated with an increased risk of maculopathy. In the univariate analysis, the HR for maculopathy was 1.7 (95% CI, 1.66–1.75), which means that patients using PPS have 70% higher risk of maculopathy compared to a patient who is not using it.
• Adjusting for confounding factors, multivariate analysis remained significant with a hazard ratio of 1.34 (95% CI, 1.31–1.38), indicating 34% increased risk among the PPS users.
• The average cumulative dose of PPS for the cohort was 37.2 ± 76.7 grams. Sensitivity analyses further confirmed the basic results: the risks of maculopathy remained increased with prolonged exposure or higher cumulative doses.
This multicenter national cohort study has established that there is a relationship between the use of pentosan polysulfate and the incidence of maculopathy in patients with cystitis. Physicians must further weigh benefits of PPS against the risk of maculopathy developing and to utilize alternative treatments when appropriate. Further research needs to occur to provide more concrete guidelines about the use of PPS in management of cystitis and long-term implications for eye health.
Reference:
Kim, M. S., Choi, Y. J., Ji, E., Song, S. H., Joo, K., Park, S. J., & Woo, S. J. (2024). Association between pentosan polysulfate and subsequent maculopathy: Insights from a nationwide population-based study in Korea. Ophthalmology.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2024.07.027
Dr Riya Dave has completed dentistry from Gujarat University in 2022. She is a dentist and accomplished medical and scientific writer known for her commitment to bridging the gap between clinical expertise and accessible healthcare information. She has been actively involved in writing blogs related to health and wellness.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


