- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Peripheral trigeminal nerve block improves symptoms of chronic orbital pain: Study
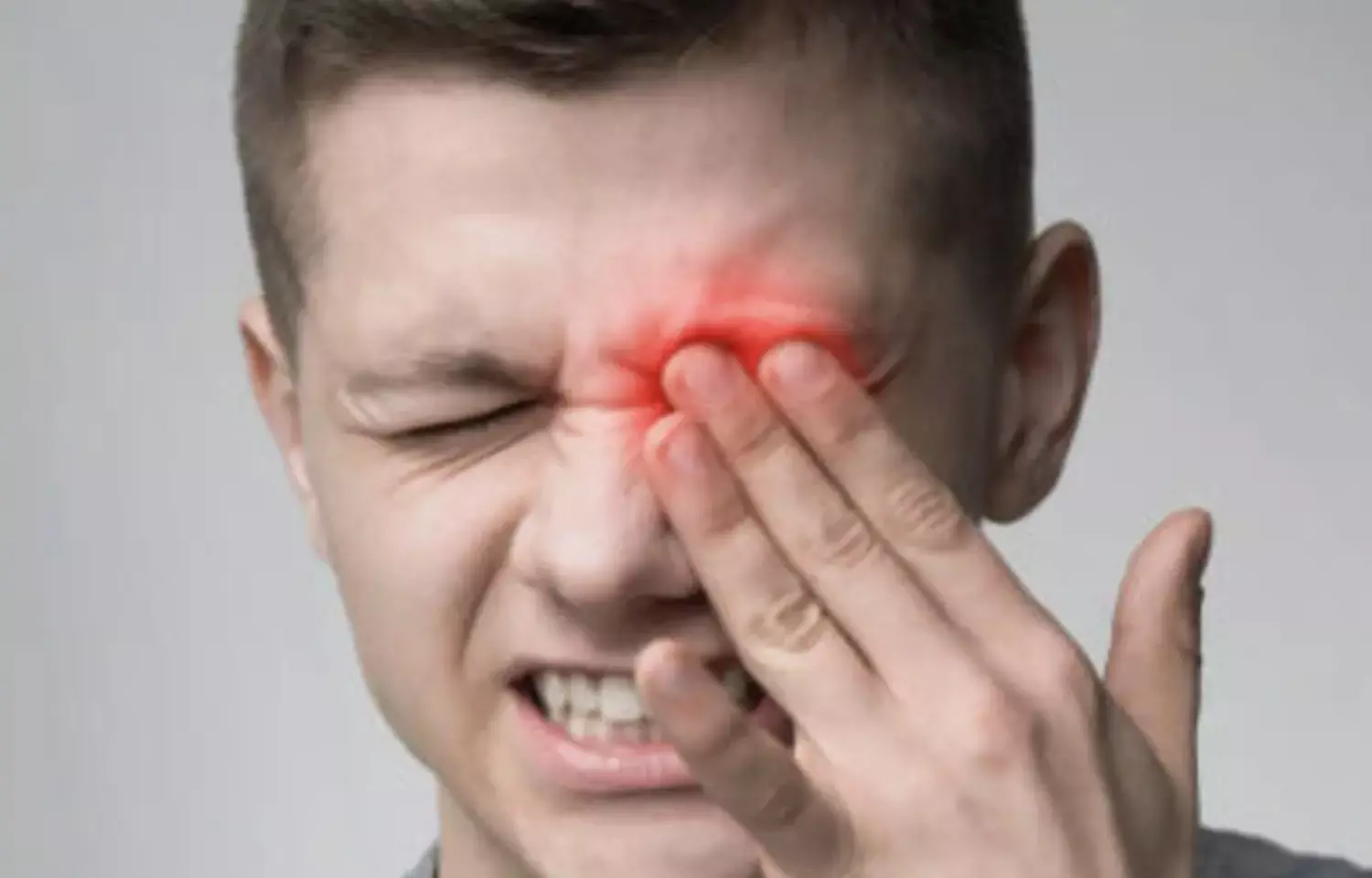
USA: Modulating trigeminal afferent nerve activity with peripheral trigeminal nerve blocks may be a favorable treatment strategy for multifactorial chronic orbital pain, states an article published in the Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstruction Surgery.
Chronic ocular pain can be seen as a manifestation of several clinical scenarios. Patients often describe ocular pain as "dryness", "burning", "tenderness", and "aching". Pain in the eye can arise from chronic ocular surface disruption and inflammation, from neuropathic processes, or frequently from mixed mechanisms. The trigeminal nerve also called the fifth cranial nerve, mediates sensations of the face and eye. A trigeminal nerve block is a type of therapeutic pain block that involves injecting a local anesthetic into the trigeminal nerve, which carries sensation from the face to the brain.
Grace Lee, University of Iowa, Iowa City, USA, and colleagues conducted a retrospective study to characterize chronic orbital pain in patients who benefitted from peripheral trigeminal nerve blocks and to explore the relationship between pain etiologies and phenotypes, injection attributes, and positive response to treatment.
Investigators included 19 patients who underwent a total of 94 peripheral trigeminal nerve blocks for chronic orbital pain in the study. Data reviewed included inciting factors, neuropathic symptoms of orbital pain, injection composition (anesthetic alone versus anesthetic + dexamethasone), and corneal epitheliopathy grades. Primary outcomes assessed were a response to injection, duration of injection effectiveness, and overall treatment efficacy. Associations between subgroups of chronic orbital pain, injection attributes, and treatment outcomes were examined. During a mean follow-up period of 2.4 years after initial injection (range 7 days-4.6 years),
Key findings of the study,
• Out of the total, 84.2% of the patients achieved either partial or complete improvement.
• Ocular versus nonocular origin of orbital pain or the presence of neuropathic sensory characteristics were not associated with a treatment outcome.
• Injections containing dexamethasone had a lower positive efficacy (relative risk-0.88) and no statistically significant association with prolonged effect.
• 50.9% of the injections for which effect duration was recorded produced a response lasting greater than 6 weeks.
Investigators conclude that giving peripheral trigeminal nerve blocks for modification of trigeminal afferent nerve activity may be a good treatment strategy for chronic orbital pain of diverse etiologies and phenotypes.
Reference:
Lee G, Pham CM, Kardon RH, Shriver EM. Peripheral Trigeminal Nerve Blocks for Chronic Orbital Pain: Clinical Features and Outcomes. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2022 Jul-Aug 01;38(4):369-376. doi: 10.1097/IOP.0000000000002120
BDS
Dr. Hiral patel (BDS) has completed BDS from Gujarat University, Baroda. She has worked in private dental steup for 8years and is currently a consulting general dentist in mumbai. She has recently completed her advanced PG diploma in clinical research and pharmacovigilance. She is passionate about writing and loves to read, analyses and write informative medical content for readers. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


