- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Rebamipide ophthalmic solution improves signs and symptoms of dry eye disease
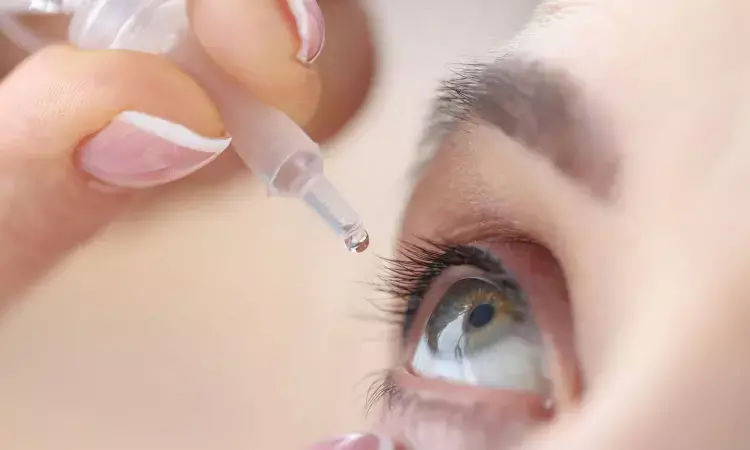
In a population of Korean patients with dry eye disease, 1% and 2% rebamipide clear ophthalmic solution applied four times a day for 12 weeks significantly improved tear break-up time and Schirmer 1 test scores, whereas the 2% concentration improved corneal staining scores, compared with placebo use.
This novel treatment is safe and effective for improving dry eye disease's clinical signs and symptoms.
This study, "Efficacy and safety of 1% and 2% rebamipide clear solution in dry eye disease: a multicenter randomized trial" by Eom et al., is published in BMC Ophthalmology.
The study evaluated the efficacy of 1% and 2% rebamipide clear solution in treating dry eye disease (DED).
Two hundred twenty patients of mean age 43 years with DED were randomly assigned to one of three groups: 1% rebamipide, 2% rebamipide, or placebo.
The tear film break-up time (TBUT), corneal and conjunctival staining score, Schirmer 1 test, and the Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI) were evaluated at baseline and at the 12-week visit to compare the efficacy of the study groups. Each eye drop was administered four times daily for 12 weeks.
The results of the study are:
- There was greater improvement in 1%, and 2% rebamipide groups showed in TBUT at 12 weeks from baseline compared to the placebo group.
- There was a more significant improvement in the 2% rebamipide group in the corneal staining score at 12 weeks from baseline than the placebo.
- At 12 weeks of treatment, the 1% and 2% rebamipide groups showed improvement in the Schirmer 1 test, compared to the placebo group, which did not exhibit any such improvement.
- The Rebamipide and placebo groups demonstrated significant improvements in OSDI after 12 weeks of treatment, but there was no significant disparity among the three groups.
They concluded that 1% and 2% rebamipide clear solutions are an effective therapeutic option for improving TBUT and tear volume and stabilizing the corneal staining score in DED.
Further reading:
https://bmcophthalmol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12886-023-03004-1
BDS, MDS in Periodontics and Implantology
Dr. Aditi Yadav is a BDS, MDS in Periodontics and Implantology. She has a clinical experience of 5 years as a laser dental surgeon. She also has a Diploma in clinical research and pharmacovigilance and is a Certified data scientist. She is currently working as a content developer in e-health services. Dr. Yadav has a keen interest in Medical Journalism and is actively involved in Medical Research writing.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


