- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Red Cell Distribution Width-to-Albumin Ratio Shows Nonlinear Link With Retinopathy Risk: Study
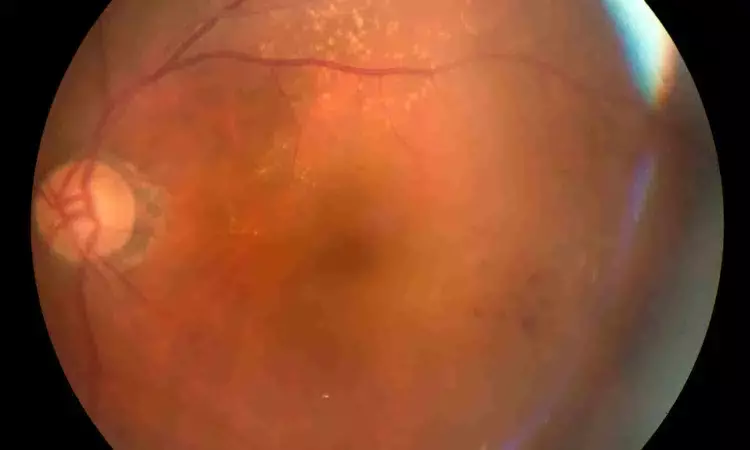
Researchers have determined that the red cell distribution width-to-albumin ratio (RAR), a composite biomarker of systemic inflammation and nutritional status, is linked to the risk of retinopathy in US adults over age 40. The new research identifies that the association between RAR and retinopathy is not linear and suggests that RAR may be a valuable tool for identifying patients at higher risk. The study was published in the Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare by Gu J. and colleagues.
Diabetic retinopathy, the diabetic complication most frequently linked to diabetes, was quantitated in diabetic and nondiabetic subjects through standardized fundus photographs and the ETDRS grading system. The information came from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2005–2008, which comprised a nationally representative sample of 4,753 adults aged 40 years and older in the United States.
This was a cross-sectional study using NHANES data from 2005 to 2008. A total of 4,753 adults aged 40 and older were included. Retinopathy was determined through retinal photographs evaluated according to the ETDRS grading protocol. RAR was estimated from laboratory data, and participants were divided into quartiles according to RAR levels. To examine the nature of the relationship between RAR and retinopathy, researchers employed generalized additive models to assess nonlinear trends, and a two-piecewise linear regression model to detect the point of inflection at which the relation changed.
Key Findings
• The univariate analysis disclosed a very pronounced increase in retinopathy prevalence in association with increasing quartiles of RAR (P < 0.001).
• A clear nonlinear relationship between RAR and retinopathy risk was observed, with an inflection point at a RAR value of 3.14.
• Below the inflection point (RAR < 3.14): With each 1-unit increase in RAR, there were 2.69 times greater odds of retinopathy (OR = 3.69; 95% CI: 1.37–9.96).
• Above the inflection point (RAR > 3.14): The relationship flattened, with a non-significant rise in odds (OR = 1.14; 95% CI: 0.60–2.14).
• Highest vs. lowest RAR quartile: Individuals with the highest quartile had 56% higher odds of retinopathy than individuals in the lowest quartile (OR = 1.56; 95% CI: 1.16–2.11).
This population-based research found that the RAR has a nonlinear correlation with the risk of retinopathy in U.S. adults aged 40 and above. The risk grew disproportionately large below an RAR value of 3.14, beyond which the association plateaued. These results uphold the promise of RAR as a simple, low-cost biomarker for retinopathy risk stratification, particularly in primary care and public health settings.
Reference:
Dr Riya Dave has completed dentistry from Gujarat University in 2022. She is a dentist and accomplished medical and scientific writer known for her commitment to bridging the gap between clinical expertise and accessible healthcare information. She has been actively involved in writing blogs related to health and wellness.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


