- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Transplantation of salivary glands may help relieve symptoms of severe dry eye disease
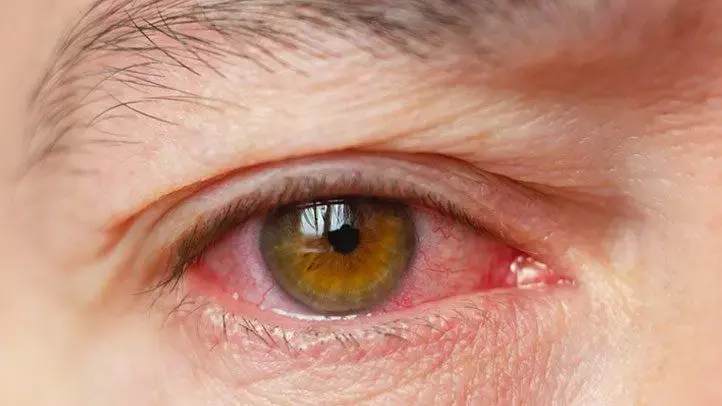
Transplantation of salivary glands should be recommended on the basis of the severity of dry eye disease according to a recent study published in the American Journal of Ophthalmology.
A study was conducted to compare submandibular gland (SMG) transplantation with minor salivary glands (MSGs) transplantation for the treatment of different dry eye diseases (DED).
Seventy-three refractory dry eye diseases eyes were divided into three groups. Group A: 35 end-stage of dry eye disease eyes who underwent SMG transplantation. Group B: 20 end-stage DED eyes with MSGs transplantation. Group C: 18 non-end-stage of dry eye disease eyes with MSGs transplantation. Schirmer test (ST), tear break-up time (TBUT), corneal fluorescein staining (FL), and best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) were measured before and after surgery.
Results:
- The length of hospital stay, length of operation, and hospital fee were significantly higher in the group
- A than in group B or C. Eyes in group A showed the most severe dry eye disease with preoperative ST, TBUT, FL, and BCVA of 0.36 mm/5min, 0.03 s, 10.97, and 0.11, respectively, which improved significantly to 20.23 mm/5min, 1.74 s, 7.58, and 0.2 at > 2 years follow-up.
- Group B had similar baseline data and significant but limited improvement only in the ST (0.55 mm/5min to 3.79 mm/5min) and FL (11.10 to 9.58) after the operation.
- Group C had better baseline ST, TBUT, FL, and BCVA of 0.89 mm/5min, 3.49 s, 1.83, and 0.81, respectively, which improved significantly (except for BCVA) to 9.35 mm/5min, 9.08 s, 0.53, and 0.89 after MSGs transplantation.
Submandibular gland transplantation could be recommended to treat end-stage refractory of dry eye disease. MSGs transplantation may provide satisfying results for refractory dry eye disease with relatively less severe impairment of the eye.
Reference:
Submandibular gland transplantation vs. minor salivary glands transplantation for treatment of dry eye: A retrospective cohort study. Salivary glands transplantations for dry eye disease by Jia-Zeng Su et al. published in the American Journal of Ophthalmology.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2022.05.019
Keywords:
Transplantation, salivary, glands, recommended, basis, severity, DED, American Journal of Ophthalmology, Submandibular gland, minor salivary glands, dry eye disease, Bang Zhang, Zhen Wang, Xiao-Jing Liu, Zhi-Gang Cai, Lei-Zhang, Xin-Peng, Jun Wu, Xin-Hua Liu, Lan Lv, Guang-Yan Yu
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


