- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Widefield Fluorescein Angiography Helps in Diagnosing Susac Syndrome
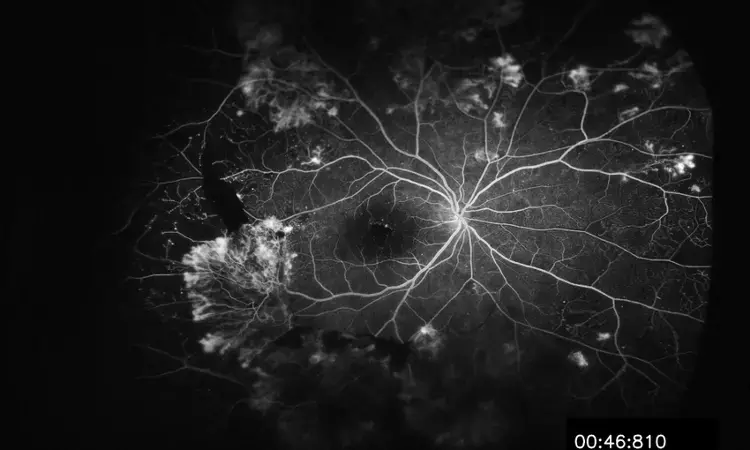
Diagnosing Susac syndrome is extremely difficult because of the rarity of the disease and the signs and symptoms that often occur at different times. In a study, researchers of Poland suggests that widefield Fluorescein angiography (WF-FA), can be helpful in the evaluation of patients referred for suspected Susac syndrome. The study findings were published in the journal RETINA, on July 2021.
Susac syndrome (SS) is a rare immune-mediated disorder that involves encephalopathy, hearing loss, and branch retinal artery occlusion. Multidisciplinary approaches and multimodal images are mandatory for diagnosis and prompt therapy. Researchers from the Infant Jesus Teaching Hospital, University Clinical Center of the Medical University of Warsaw, Poland conducted a study to present the clinical manifestations and results of key diagnostic investigations in patients with Susac syndrome, with special emphasis on the principal role of fluorescein angiography (FA) of the peripheral retina.
In this retrospective analysis of medical records, the researchers evaluated 20 patients (15 women and five men), aged 20 to 51 years with complete or incomplete Susac syndrome diagnosed by an ophthalmic examination and widefield fluorescein angiography (WF-FA) by Spectralis and Optos Tx200.
Key Findings of the Study Were:
- Upon analysis, the researchers found that fluorescein angiography abnormalities included vascular changes in the posterior pole in 64.7% and the peripheral retina in 82.4%.
- They observed widefield FA abnormalities in 35% of peripheral retinas and posterior poles but without peripheral involvement in 17.6% of eyes.
- They noted secondary leakage from veins in 58.8%
They noted, "Widefield FA of the peripheral retina has a key role in cases of suspected Susac syndrome as it confirms the diagnosis and assesses disease activity. In addition to the characteristic findings, late-phase FA revealed leakage from veins which is not a typical sign."
The authors concluded, "Patients experiencing migraine headaches may benefit from increasing awareness of neurologists and otologists who more promptly referred patients with suspected Susac syndrome for ophthalmologic evaluation and WF-FA of the peripheral retina."
For further information:
Medical Dialogues Bureau consists of a team of passionate medical/scientific writers, led by doctors and healthcare researchers. Our team efforts to bring you updated and timely news about the important happenings of the medical and healthcare sector. Our editorial team can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


