- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Alcohol consumption tied to tophi development in gout patients: Study
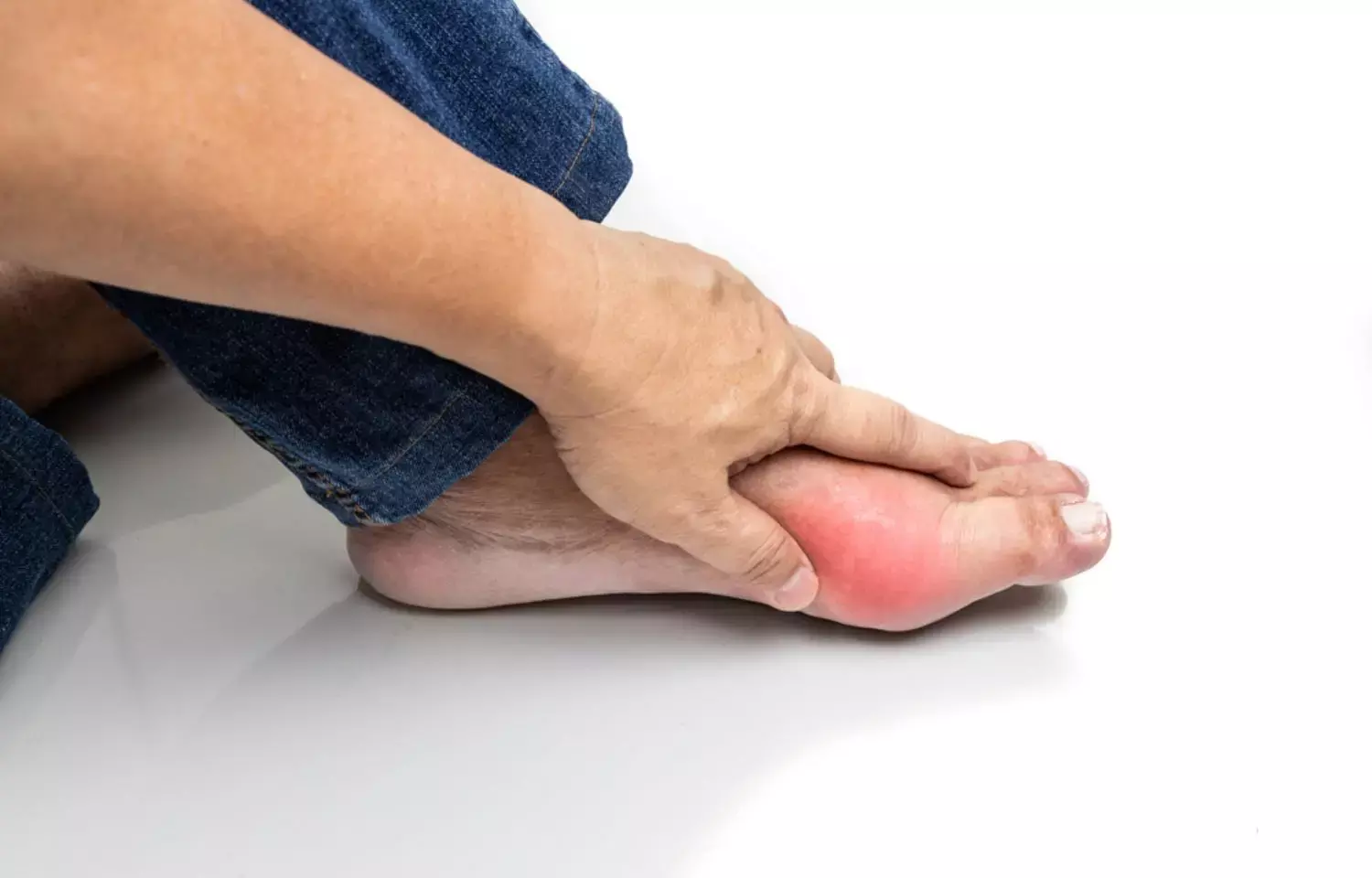
China: In patients with gout, longer duration and higher quantity of alcohol consumption as well as spirits consumption are predictors for the development of ultrasound (US)-detected tophi and sub-tophi, states an article published in the Arthritis Care & Research.
Gout is an inflammatory and metabolic disease, characterized by the deposition of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals called tophi. About 12–35% of people with gout tend to develop tophi. Tophi present as large bumps, where uric acid gout crystals have accumulated and settled in one or more joints, or subcutaneous and other tissues.
Tophi may be underdiagnosed because they are hard to find with only a physical examination. Recent studies support the positive role of ultrasound in the early diagnosis of gout and in monitoring treatment response as it is sensitive to detecting MSU deposition. All types of alcohol are known to affect gout, but the impact on flares and symptoms may vary by type of alcohol. Even a light-to-moderate amount, triggers recurrent gout attacks. Studies have shown that excessive alcohol intake may substantially increase blood uric acid levels and promote tophi formation.
Lin Han, Qingdao University, China and colleagues conducted a study to examine the association of alcohol consumption with the presence and development of ultrasound (US)-detected tophi and subcutaneous tophi (sub-tophi) in gout patients
Researchers included a total of 554 patients with gout who underwent the US and physical examination on the most frequently involved joints in gout for the present study. Multivariable analysis was performed to assess the associations of the duration, quantity, and type of alcohol consumption with the presence, size, and the number of US-detected tophi and sub-tophi.
Key findings of the study,
• Compared with non-drinkers, excessive drinkers (>70 g/week), long-term drinkers (≥10 years), and spirits drinkers had a greater proportion, size, and number of US-detected tophi and sub-tophi.
• After adjusting for confounders, excessive drinking (OR-1.79; OR: 2.00), long-term alcohol consumption (OR: 1.96; OR: 2.17), and spirits consumption of (OR: 1.81; OR: 2.10) were significantly associated with the presence of US-detected tophi and sub-tophi, with the highest OR among the identified risk factors.
• Among patients who already had US-detected tophi or sub-tophi, moderate drinking (≤ 70 g/week) was associated with larger or multiple tophi.
The authors conclude that determining the amount and duration of alcohol consumption as well as spirits consumption can help to predict the development of US-detected tophi and sub-tophi in patients with gout. Among people who have US-detected tophi and sub-tophi, weekly alcohol consumption leads to the development of tophi regardless of the amount consumed.
Reference:
Lin Han PhD,Runze Li MD,Jie Lu PhD,Wei Ren MD,Chunping Ning PhD,Jingyuan Pang BD,Jian Sun MD,Yao Wang MD,Wenyan Sun PhD,Zhen Liu PhD,Can Wang MD,Xuefeng Wang MD. First published: 13 June 2022 https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.24968
BDS
Dr. Hiral patel (BDS) has completed BDS from Gujarat University, Baroda. She has worked in private dental steup for 8years and is currently a consulting general dentist in mumbai. She has recently completed her advanced PG diploma in clinical research and pharmacovigilance. She is passionate about writing and loves to read, analyses and write informative medical content for readers. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


