- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Amniotic membrane/umbilical cord particulate injection provides pain relief for achilles tendinopathy: Study
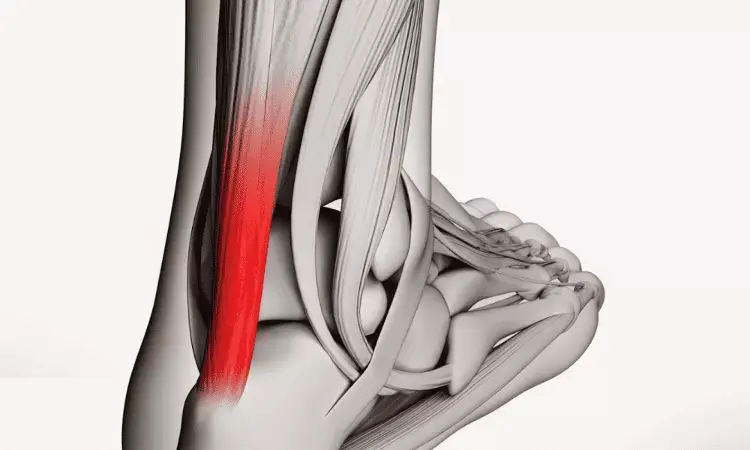
Chicago, USA: Achilles tendinopathy is a significant cause of disability among adults. Among these tendinopathy cases, 4-23% will also have concurrent partial tendon tears. Current conservative treatment modalities include analgesics, rest, orthotics, and physical therapy including eccentric exercise for tendinopathy. When non-invasive treatments fail, injectional therapy with saline, analgesics, or corticosteroid have been considered. However, there is a lack of established efficacy for conservative treatment modalities as evidenced by the wide range of reported success in literature, ranging from 24% to 89%. Furthermore, corticosteroids should be generally avoided as they may increase the risk of injury, atrophy, and decrease tendon strength.
The study by M.J. Chin and K. LaViolette investigated the alternative use of amniotic membrane/umbilical cord particulate (AMUC) injection in patients with Achilles tendinopathy with or without partial tendon tear.
Method: A single-center, retrospective study was conducted on Achilles tendinopathy patients with or without a partial tendon tear and received AMUC injection. Pain was evaluated before and after treatment, and measured on an 11-point numerical rating scale, where 0 was no pain and 10 was worst imaginable pain. Usage of pain medication and complications was also reported.
Results:
• Ten Achilles tendinopathy patients (aged 61.3 ± 11.3 years) with (n=3) or without (n=7) partial tendon tear were included in the analysis.
• The cohort's average baseline pain score was 4.8 ± 1.2 despite the majority (n=9) of patients receiving prior conservative treatment over a duration of 78.3 ± 77.6 days.
• After AMUC injection, the pain significantly decreased to 1.7 ± 1.9 at 1 month and 1.1 ± 1.4 at 3-months (p<0.01) post-treatment.
• Four patients who had previously used narcotic pain medication discontinued use within 3-months after treatment.
• There were no treatment-related complications.
The authors concluded that the use of injectable AMUC may safely provide pain relief in Achilles tendinopathy patients with or without partial tendon tear. Additional comparative studies with larger treatment groups are warranted to validate these findings.
Further reading:
Amniotic membrane/ umbilical cord particulate injection for Achilles tendinopathy with or without a partial tear
Michael J. Chin, Kathryn LaViolette.
Foot & Ankle Surgery: Techniques, Reports & Cases 2 (2022) 100169
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fastrc.2022.100169
MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS
Dr Supreeth D R (MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS) is a practicing orthopedician with interest in medical research and publishing articles. He completed MBBS from mysore medical college, dip ortho from Trivandrum medical college and sec. DNB from Manipal Hospital, Bengaluru. He has expirence of 7years in the field of orthopedics. He has presented scientific papers & posters in various state, national and international conferences. His interest in writing articles lead the way to join medical dialogues. He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


